- 1. Heroku account 취득
- 2. Node.js & npm install 확인
- 3. Heroku CLI 설치
- 4. Heroku 로그인
- 5. sample app의 준비
- 6. Deploy App
- 7. Procfile
- 8. local 환경에서의 Code의 수정과 Heroku에의 Deploy
- 9. GitHub Integration
- 10. Add-on 설치
- 11. Database 설치
- Reference

Heroku는 AWS의 IaaS 상에 구축된 PaaS이다. Git로 deploy가 가능하며 Web app 개발에서 공개까지 간단히 사용할 수 있는 Platform이다.
소규모 사이트나 개인 블로그 정도는 충분히 무료로 사용할 수 있는 공간이 주어진다.
1. Heroku account 취득
Heroku에서 sign up을 실시하여 account를 취득한다.
2. Node.js & npm install 확인
node.js와 npm, git가 사전에 install되어 있어야 한다. install 여부를 확인한다.
$ node -v
v6.9.4
$ npm -v
4.2.0
$ git --version
git version 2.6.4 (Apple Git-63)
3. Heroku CLI 설치
Heroku CLI(a.k.a. Heroku Toolbelt)는 command line/shell에서 Heroku 애플리케이션을 생성하고 관리할 수 있는 도구이다.
자신의 사양에 맞는 Heroku CLI를 설치한다.
4. Heroku 로그인
터미널에서 Heroku에 로그인한다.
$ heroku login
Enter your Heroku credentials.
Email: ungmo2@gmail.com
Password (typing will be hidden):
Logged in as ungmo2@gmail.com
5. sample app의 준비
Sample app을 clone한다. app의 이름은 나중에 수정이 가능하므로 지금은 heroku-express-example이라는 이름의 app을 생성한다.
$ git clone https://github.com/heroku/node-js-getting-started.git heroku-express-example
$ cd heroku-express-example
$ ls -al
total 56
drwxr-xr-x 12 leeungmo staff 408 2 24 00:23 .
drwxr-xr-x+ 71 leeungmo staff 2414 2 24 00:23 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 8 2 24 00:23 .env
drwxr-xr-x 13 leeungmo staff 442 2 24 00:23 .git
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 133 2 24 00:23 .gitignore
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 19 2 24 00:23 Procfile
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 1371 2 24 00:23 README.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 301 2 24 00:23 app.json
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 460 2 24 00:23 index.js
-rw-r--r-- 1 leeungmo staff 485 2 24 00:23 package.json
drwxr-xr-x 5 leeungmo staff 170 2 24 00:23 public
drwxr-xr-x 4 leeungmo staff 136 2 24 00:23 views
6. Deploy App
app을 Heroku에 생성한다. app의 이름을 지정하지 않으면 random한 이름이 자동으로 생성된다.
$ heroku create heroku-express-example
Creating ⬢ heroku-express-example... done
https://heroku-express-example.herokuapp.com/ | https://git.heroku.com/heroku-express-example.git
이제 app이 Heroku에 생성되었고 Heroku와 로컬 git 저장소는 연결된다.
이때 .git/config 파일에 아래 내용이 추가된다.
[remote "heroku"]
url = https://git.heroku.com/heroku-express-example.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/heroku/*
Sample app을 Heroku로 push한다. 이것이 바로 deploy이다.
$ git push heroku master
Counting objects: 456, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Writing objects: 100% (6/6), 695 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 6 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: Compressing source files... done.
remote: Building source:
remote:
remote: -----> Node.js app detected
remote:
remote: -----> Creating runtime environment
remote:
remote: NPM_CONFIG_LOGLEVEL=error
remote: NPM_CONFIG_PRODUCTION=true
remote: NODE_ENV=production
remote: NODE_MODULES_CACHE=true
remote:
remote: -----> Installing binaries
remote: engines.node (package.json): unspecified
remote: engines.npm (package.json): unspecified (use default)
remote:
remote: Resolving node version (latest stable) via semver.io...
remote: Downloading and installing node 5.11.1...
remote: Using default npm version: 3.8.6
remote:
remote: -----> Restoring cache
remote: Skipping cache restore (new runtime signature)
remote:
remote: -----> Building dependencies
remote: Installing node modules (package.json)
remote: express-skeletion@0.0.1 /tmp/build_08cf53544f91bec4bcfe881762701b40
remote: └─┬ express@4.14.0
remote: ├─┬ accepts@1.3.3
remote: │ ├─┬ mime-types@2.1.11
remote: │ │ └── mime-db@1.23.0
remote: │ └── negotiator@0.6.1
remote: ├── array-flatten@1.1.1
remote: ├── content-disposition@0.5.1
remote: ├── content-type@1.0.2
remote: ├── cookie@0.3.1
remote: ├── cookie-signature@1.0.6
remote: ├─┬ debug@2.2.0
remote: │ └── ms@0.7.1
remote: ├── depd@1.1.0
remote: ├── encodeurl@1.0.1
remote: ├── escape-html@1.0.3
remote: ├── etag@1.7.0
remote: ├─┬ finalhandler@0.5.0
remote: │ ├── statuses@1.3.0
remote: │ └── unpipe@1.0.0
remote: ├── fresh@0.3.0
remote: ├── merge-descriptors@1.0.1
remote: ├── methods@1.1.2
remote: ├─┬ on-finished@2.3.0
remote: │ └── ee-first@1.1.1
remote: ├── parseurl@1.3.1
remote: ├── path-to-regexp@0.1.7
remote: ├─┬ proxy-addr@1.1.2
remote: │ ├── forwarded@0.1.0
remote: │ └── ipaddr.js@1.1.1
remote: ├── qs@6.2.0
remote: ├── range-parser@1.2.0
remote: ├─┬ send@0.14.1
remote: │ ├── destroy@1.0.4
remote: │ ├─┬ http-errors@1.5.0
remote: │ │ ├── inherits@2.0.1
remote: │ │ └── setprototypeof@1.0.1
remote: │ └── mime@1.3.4
remote: ├── serve-static@1.11.1
remote: ├─┬ type-is@1.6.13
remote: │ └── media-typer@0.3.0
remote: ├── utils-merge@1.0.0
remote: └── vary@1.1.0
remote:
remote:
remote: -----> Caching build
remote: Clearing previous node cache
remote: Saving 2 cacheDirectories (default):
remote: - node_modules
remote: - bower_components (nothing to cache)
remote:
remote: -----> Build succeeded!
remote: └── express@4.14.0
remote:
remote: -----> Discovering process types
remote: Procfile declares types -> web
remote:
remote: -----> Compressing...
remote: Done: 12.1M
remote: -----> Launching...
remote: Released v3
remote: https://heroku-express-example.herokuapp.com/ deployed to Heroku
remote:
remote: Verifying deploy... done.
To https://git.heroku.com/heroku-express-example.git
* [new branch] master -> master
app이 deploy되었다. deploy될 때 package.json의 dependency가 자동으로 install된다.
instance가 동작하고 있지 않으면 다음 명령어로 기동시킨다.
$ heroku ps:scale web=1
Scaling dynos... done, now running web at 1:Free
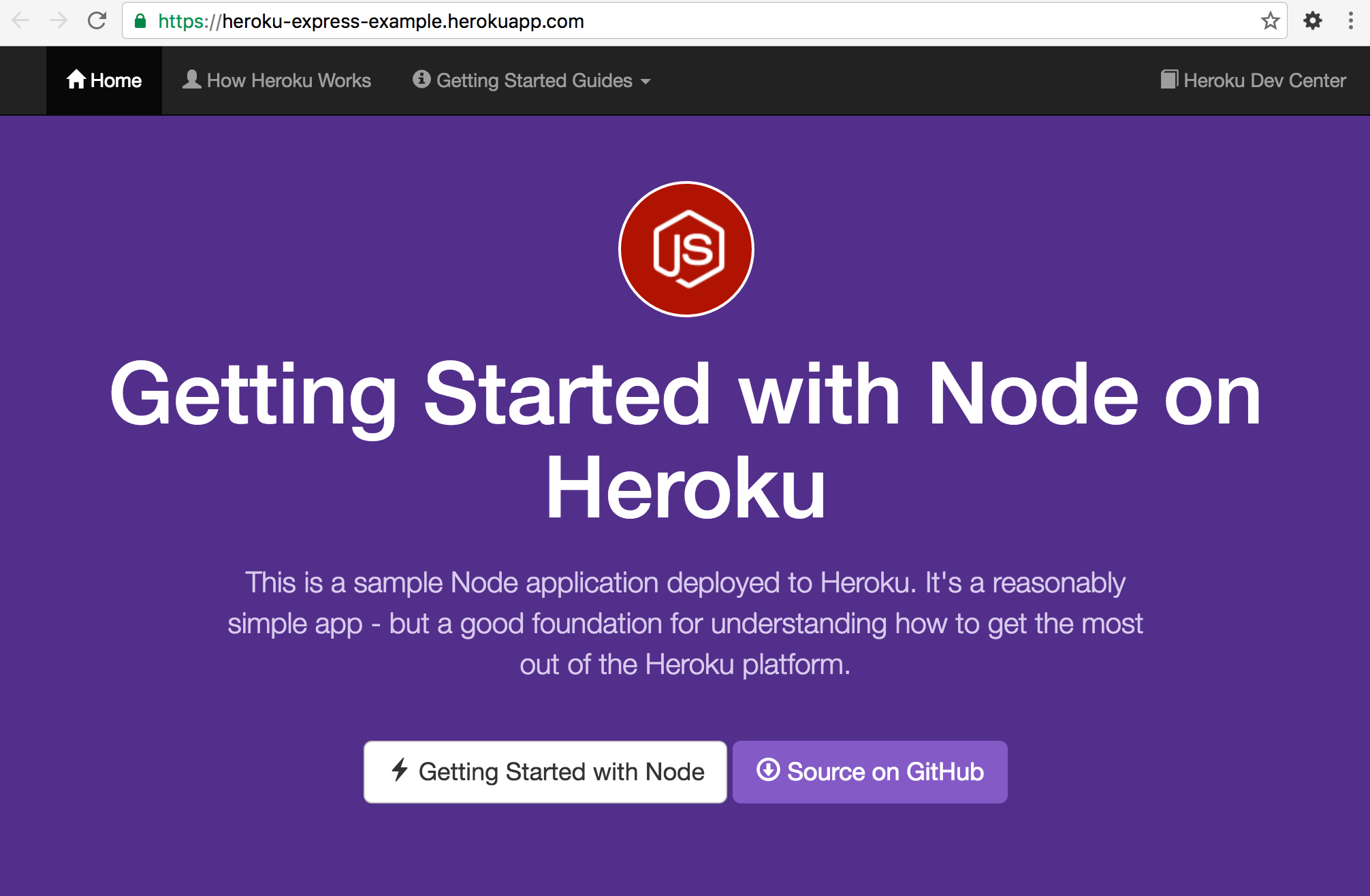
이제 생성된 app이 동작하는 URL으로 방문하여 동작을 확인한다. 또는 아래의 명령어로 방문할 수 있다.
$ heroku open
log를 확인하는 방법은 아래와 같다.
$ heroku logs --tail
7. Procfile
루트 디렉터리에 있는 Procfile에는 app이 start할 때 실행하여야 하는 동작을 명시적으로 정의한다.
web: node index.js
web은 process type을 의미한다.
8. local 환경에서의 Code의 수정과 Heroku에의 Deploy
8.1 local 환경 구축
local 환경에서 code를 수정하고 local 환경에서 app을 기동하여 수정사항을 확인한 후 Heroku에 수정사항을 반영한다.
local 환경을 구축하기 위하여 필요에 따라 pakage.json의 dependency 설정을 변경하고 local 환경에 필요 dependency를 설치한다.
{
"name": "node-js-getting-started",
"version": "0.2.5",
...
"engines": {
"node": "5.9.1"
},
"dependencies": {
"ejs": "2.4.1",
"express": "4.13.3"
},
...
}
$ cd heroku-express-example
$ npm install
heroku local command를 사용하여 local에서 app을 기동한다.
$ heroku local web
[OKAY] Loaded ENV .env File as KEY=VALUE Format
17:15:52 web.1 | Node app is running on port 5000
반드시 heroku 명령어를 사용해야 하는 것은 아니다. 아래와 같이 일반적인 방법도 가능하다.
$ npm start
브라우저에서 http://localhost:5000으로 접속하여 local 환경에서 app이 실행되었음을 확인한다.
8.2 Code의 수정
code를 수정한다.
cool-ascii-faces를 install한다.
$ npm install --save --save-exact cool-ascii-faces
index.js를 아래와 같이 수정한다. ool-ascii-faces를 require하고 /cool 라우트를 추가한다.
var cool = require('cool-ascii-faces');
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.set('port', (process.env.PORT || 5000));
app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'));
// views is directory for all template files
app.set('views', __dirname + '/views');
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
app.get('/', function(request, response) {
response.render('pages/index')
});
app.get('/cool', function(request, response) {
response.send(cool());
});
app.listen(app.get('port'), function() {
console.log('Node app is running on port', app.get('port'));
});
$ npm install
$ heroku local web
브라우저에서 http://localhost:5000/cool으로 접속하여 local 환경에서 app이 실행되었음을 확인한다.
( ⚆ _ ⚆ )
8.3 Heroku에의 Deploy
먼저 모든 파일을 local git에 추가한다.
$ git add .
수정사항을 repository에 commit한다.
$ git commit -m "Demo"
heroku master에 git push한다.
$ git push heroku master
$ git push origin master
app을 실행시켜서 정상 작동됨을 확인한다.
$ heroku open cool
9. GitHub Integration
github와 연동하여 heroku에 수정사항을 반영할 수 있다.
Heroku Dashboard의 Deploy 탭으로 이동한다.
Deployment method에서 GitHub를 선택한다.
Connect to GitHub에 자신의 github repository를 등록한다.
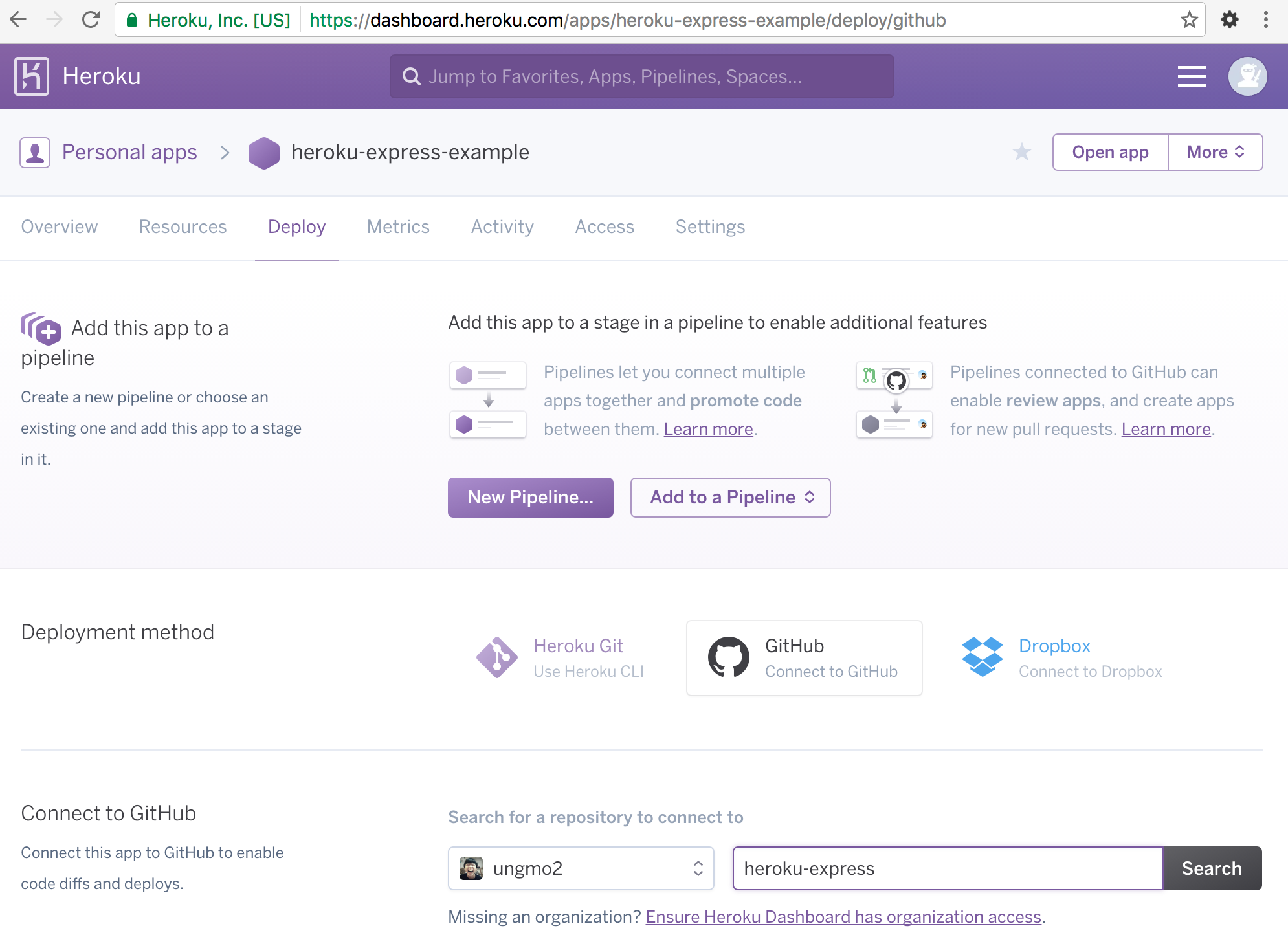
Connect to GitHub의 Search 버튼을 클릭하여 github repository를 등록한 후 Connect 버튼을 클릭한다.
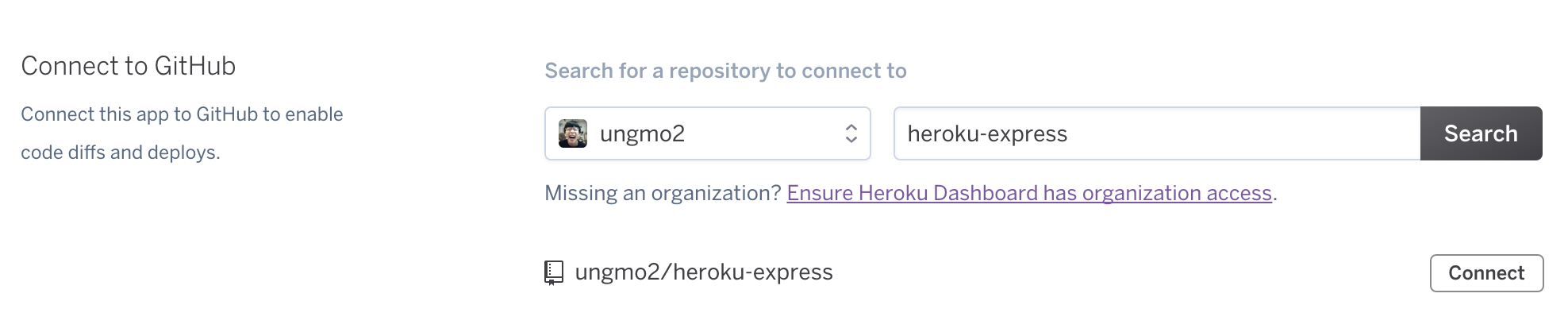
Automatic deploys에서 Enable Automatic Deploys 버튼을 클릭한다.
이후 code를 GitHub에 push하면 자동으로 Heroku에 deploy가 실행된다.
10. Add-on 설치
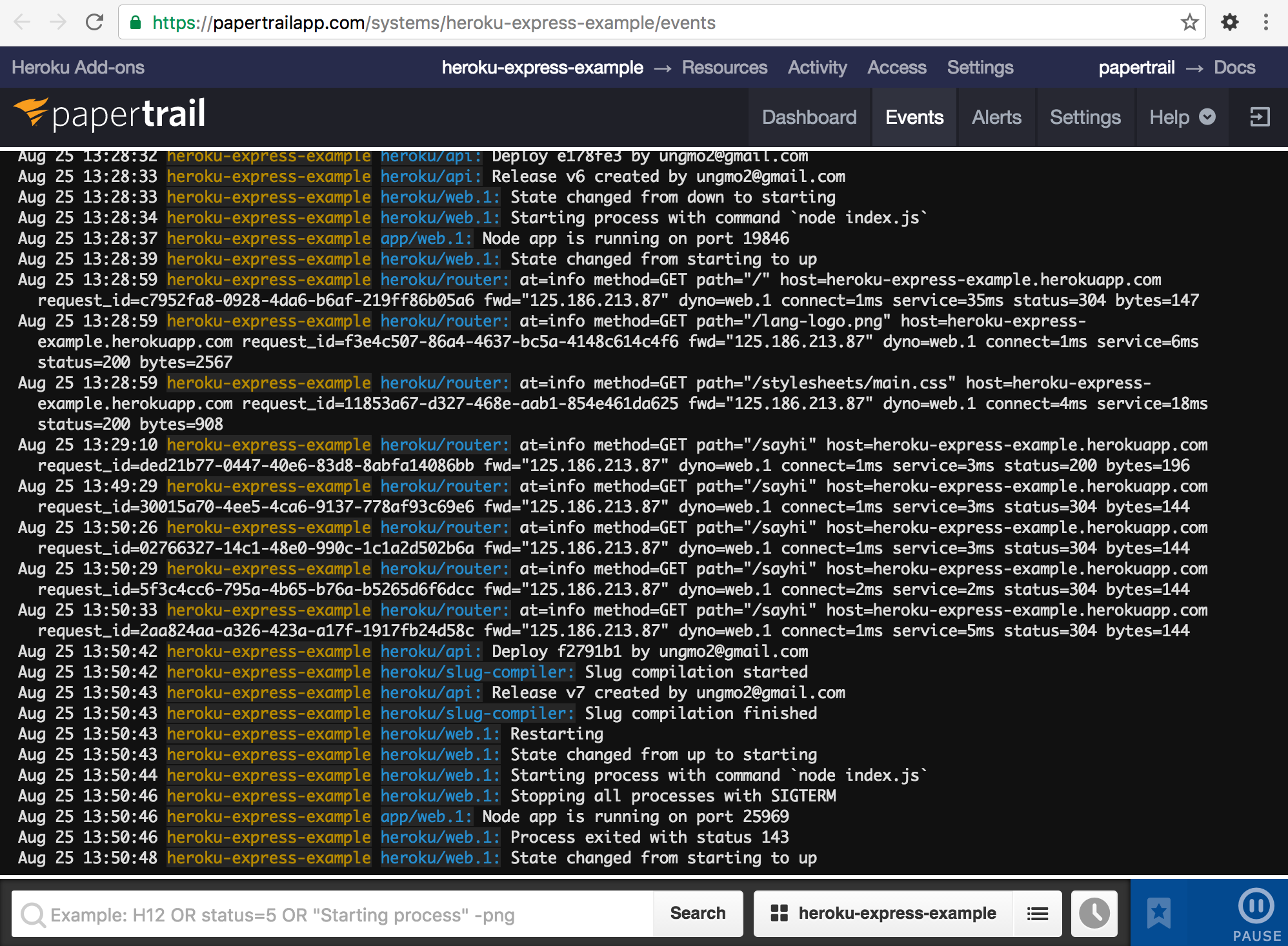
Logging add-on Papertrail을 설치한다.
$ heroku addons:create papertrail
$ heroku addons
Add-on Plan Price
────────────────────────────────────── ─────── ─────
papertrail (papertrail-colorful-87606) choklad free
└─ as PAPERTRAIL
The table above shows add-ons and the attachments to the current app (heroku-express-example) or other apps.
$ heroku addons:open papertrail
11. Database 설치
Heroku는 Redis, MongoDB, Postgres, MySQL 등 다수의 data store add-on을 제공한다.
이중 MongoDB add-on을 추가한다.
$ heroku addons:create mongolab
또는 아래와 같이 추가할 수도 있다.
https://elements.heroku.com/addons으로 이동하여 mLab MongoDB를 선택한다.
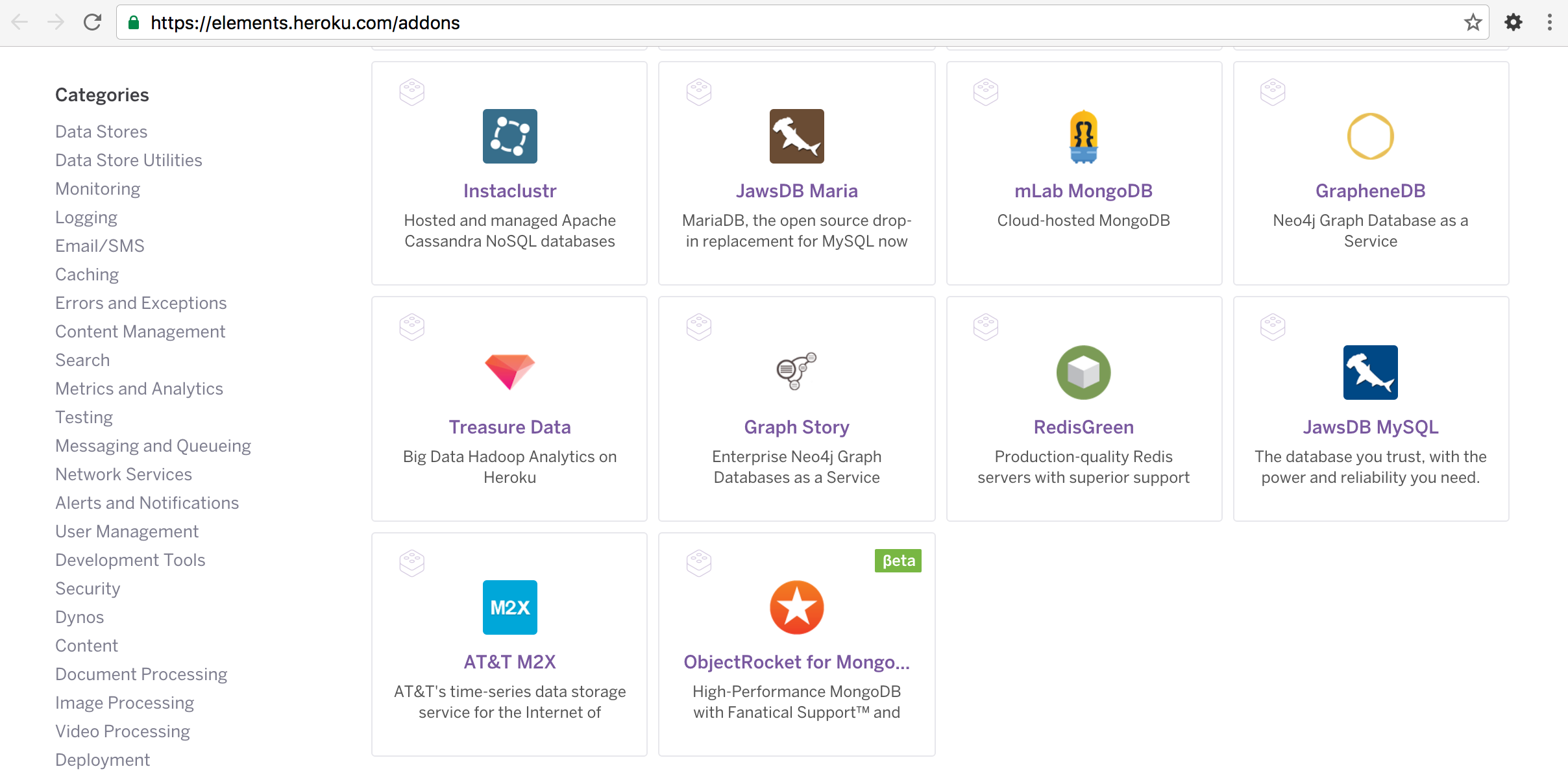
Install mLab MongoDB 버튼을 클릭한다.
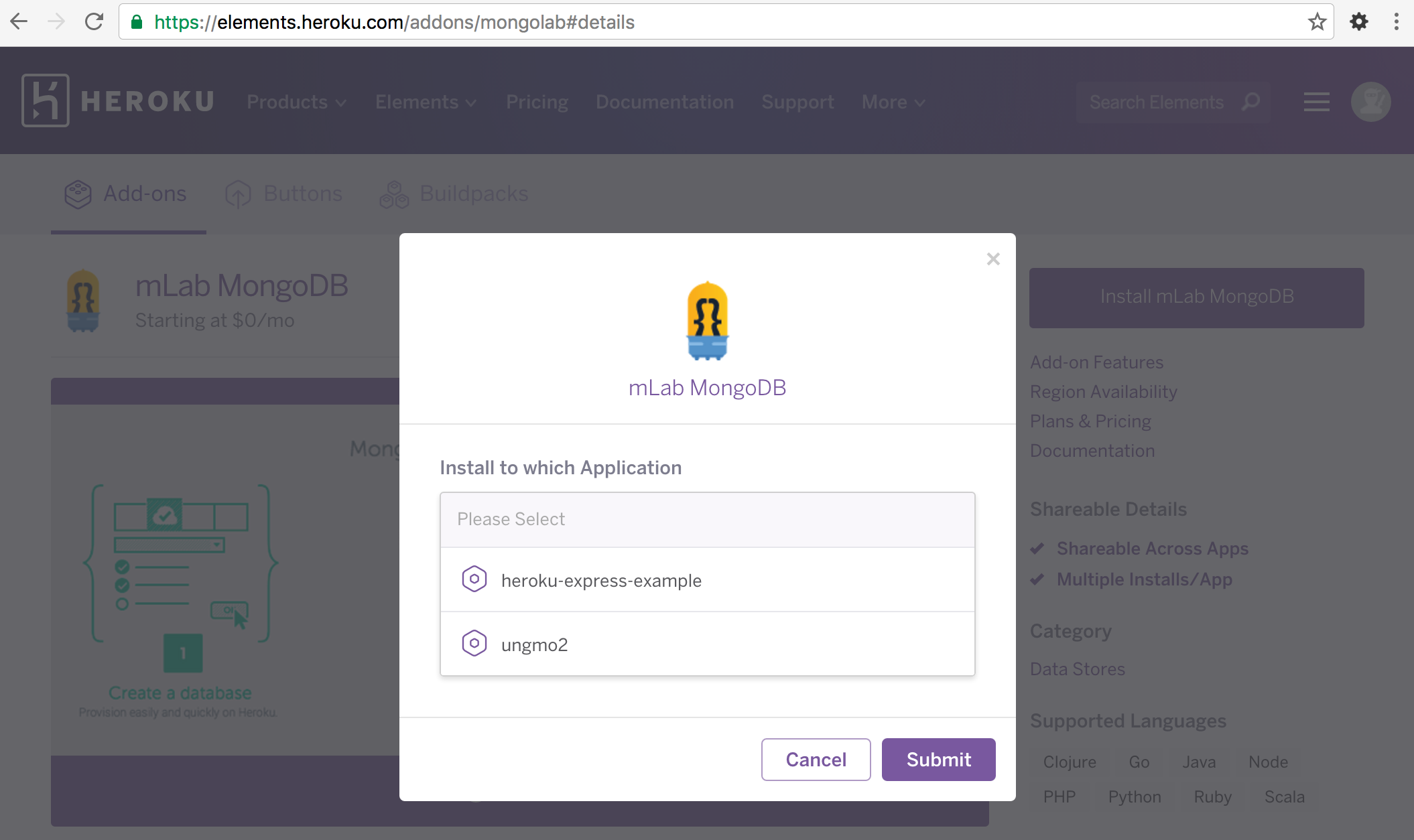
Install 대상 app을 선택한다.
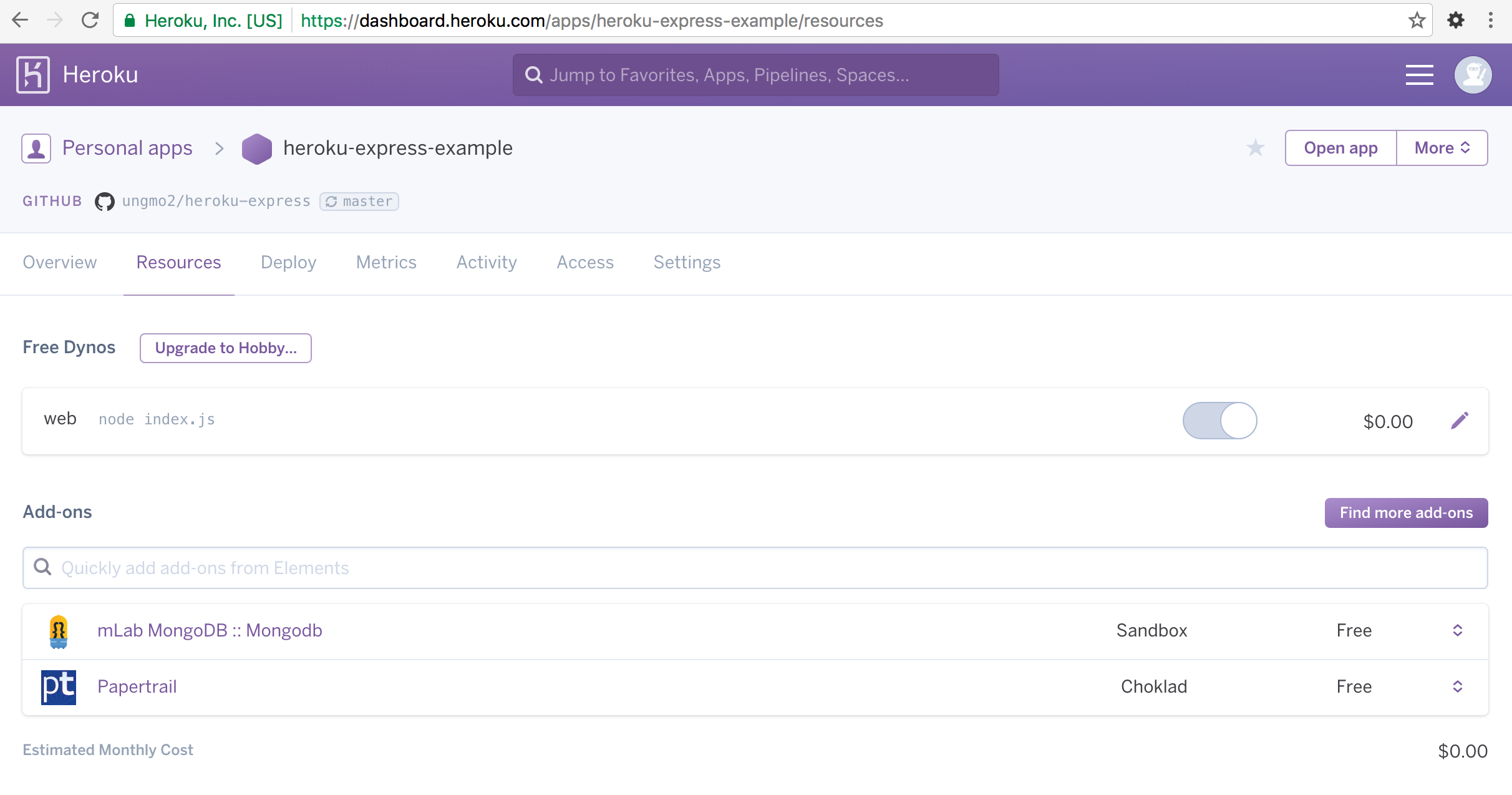
Heroku Dashboard의 Resources 탭으로 이동하여 Add-ons의 mLab MongoDB를 클릭한다.
Users 탭을 선택하고 Add database user 버튼을 클릭하여 새로운 사용자를 생성한다.
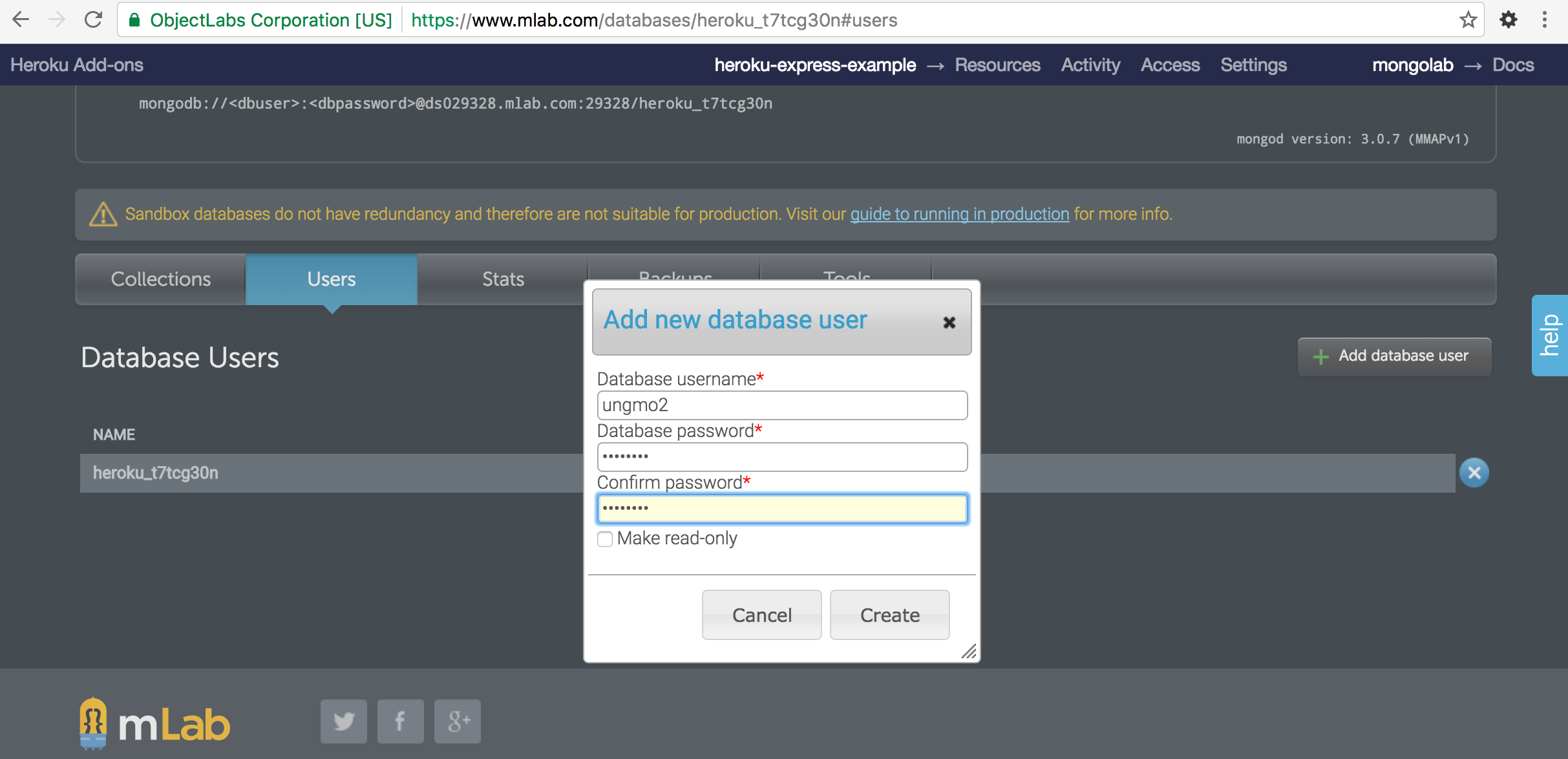
MongoDB add-on을 생성하면 database connection URI이 config var에 저장된다.
이 값은 Node.js 내에서 process.env.MONGODB_URI로 접근할 수 있다.
새롭게 생성한 user를 config var의 MONGODB_URI에 저장한다.
MongoDB에 접속한다.
$ mongo ds029328.mlab.com:29328/<dbname> -u <dbuser> -p <dbpassword>
MongoDB shell version: 3.2.8
connecting to: ds029328.mlab.com:29328/heroku_t7tcg30n
rs-ds029328:PRIMARY>
sample data를 insert한다.
use heroku_t7tcg30n
switched to db heroku_t7tcg30n
rs-ds029328:PRIMARY> db.books.insert(
[{ title: "Example1", author: "Lee", price: 100 },
{ title: "Example2", author: "Kim", price: 200 },
{ title: "Example3", author: "Choi", price: 300 },
{ title: "Example4", author: "Park", price: 400 }])
BulkWriteResult({
"writeErrors" : [ ],
"writeConcernErrors" : [ ],
"nInserted" : 4,
"nUpserted" : 0,
"nMatched" : 0,
"nModified" : 0,
"nRemoved" : 0,
"upserted" : [ ]
})
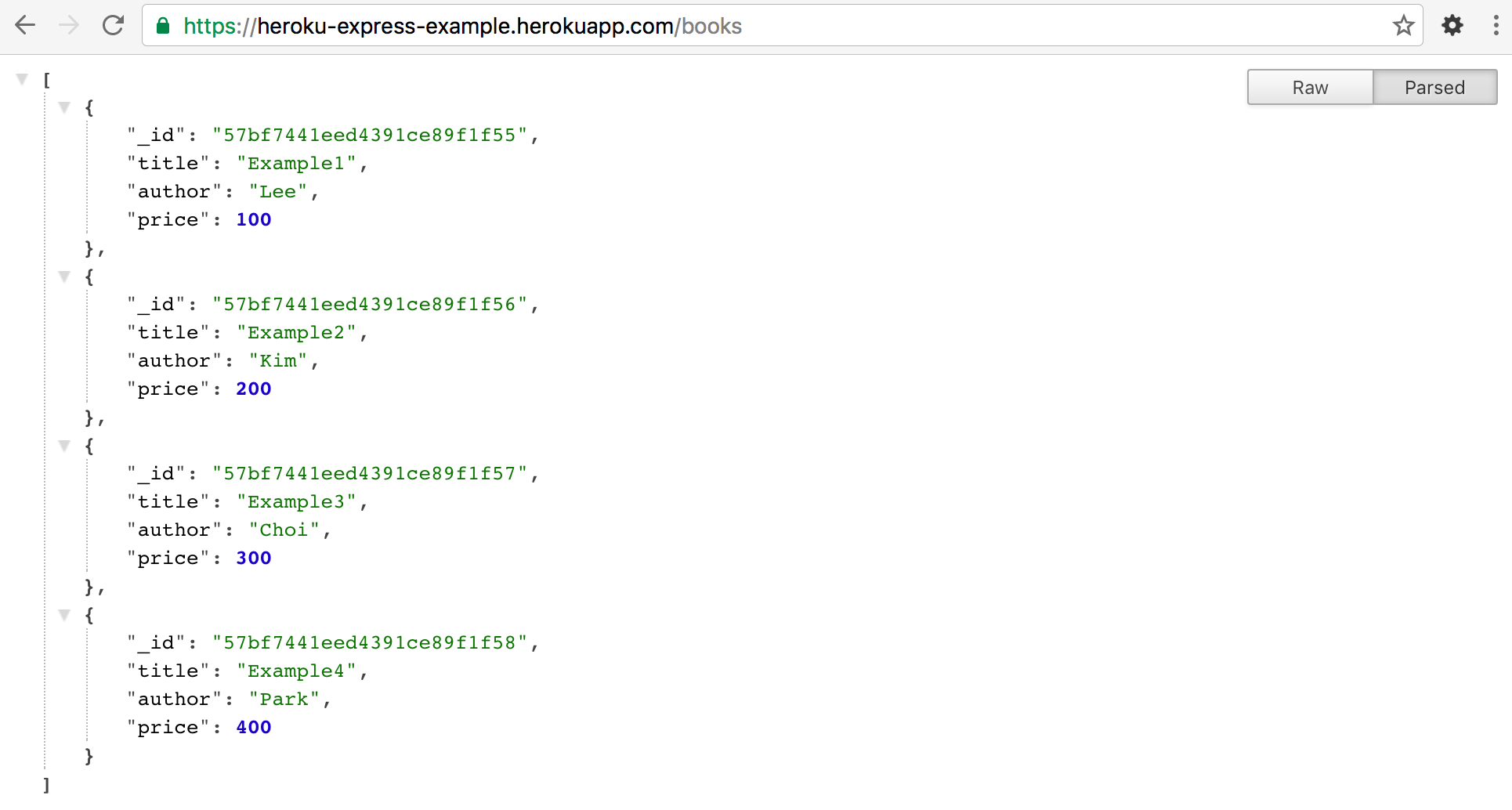
rs-ds029328:PRIMARY> db.books.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("57bf7441eed4391ce89f1f55"), "title" : "Example1", "author" : "Lee", "price" : 100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("57bf7441eed4391ce89f1f56"), "title" : "Example2", "author" : "Kim", "price" : 200 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("57bf7441eed4391ce89f1f57"), "title" : "Example3", "author" : "Choi", "price" : 300 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("57bf7441eed4391ce89f1f58"), "title" : "Example4", "author" : "Park", "price" : 400 }
rs-ds029328:PRIMARY>
mongoose 모듈을 install한다.
$ npm install --save --save-exact mongoose
index.js를 수정한다.
var cool = require('cool-ascii-faces');
var express = require('express');
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
var app = express();
app.set('port', (process.env.PORT || 5000));
app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'));
// views is directory for all template files
app.set('views', __dirname + '/views');
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
// CONNECT TO MONGODB SERVER
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGODB_URI);
// DEFINE MODEL
var Books = require('./models/books');
app.get('/', function(request, response) {
response.render('pages/index');
});
app.get('/cool', function(request, response) {
response.send(cool());
});
// GET ALL BOOKS
app.get('/books', function(req,res){
Books.find(function(err, books){
if(err) return res.status(500).send({error: 'database failure'});
res.json(books);
});
});
app.listen(app.get('port'), function() {
console.log('Node app is running on port', app.get('port'));
});
root 디렉터리에 models 디렉터리를 생성하고 books.js를 생성하여 추가한다.
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var booksSchema = new Schema({
title : String,
author: String,
price : Number
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('books', booksSchema);
Heroku에 deploy 후 동작을 확인한다.