이전에는 table을 사용하여 layout을 만들기도 하였으나 html과 css의 본연의 취지와도 맞지 않을 뿐더러 반응형 웹 페이지 작성이 곤란하며 코드의 양 또한 많아져 현재는 거의 사용하지 않는다. 모던한 웹 페이지는 style과 layout을 담당하는 CSS를 사용하여 layout을 구성하는 것이 바람직하다.
layout의 핵심은 블록 레벨 요소들을 원하는 위치에 배열하는 것이다.

Layout Examples
모바일 사용자가 데스크탑 사용자보다 많은 상황을 감안하여 화면의 크기에 따라 적절히 화면 구성을 변화시키는 반응형 웹 디자인(Responsive Web Design) 또한 모던 웹 사이트의 필수 사항이 되었다.
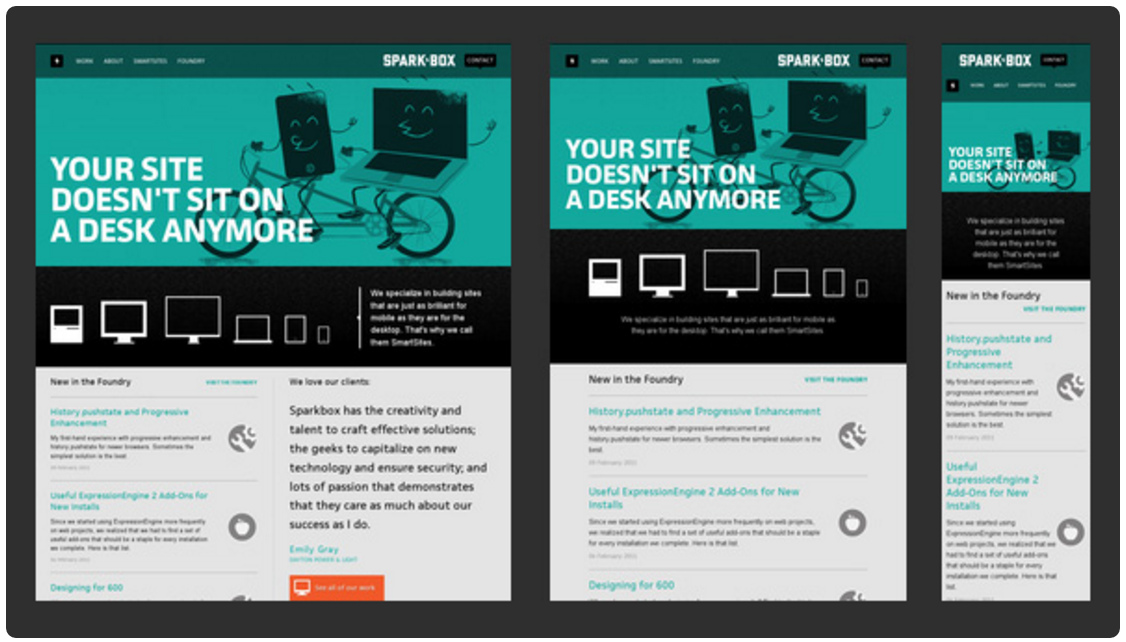
CSS를 사용하여 layout을 구성할 때에 자주 사용되는 핵심 기술은 float이다. 다음은 전형적인 웹사이트의 layout이다.
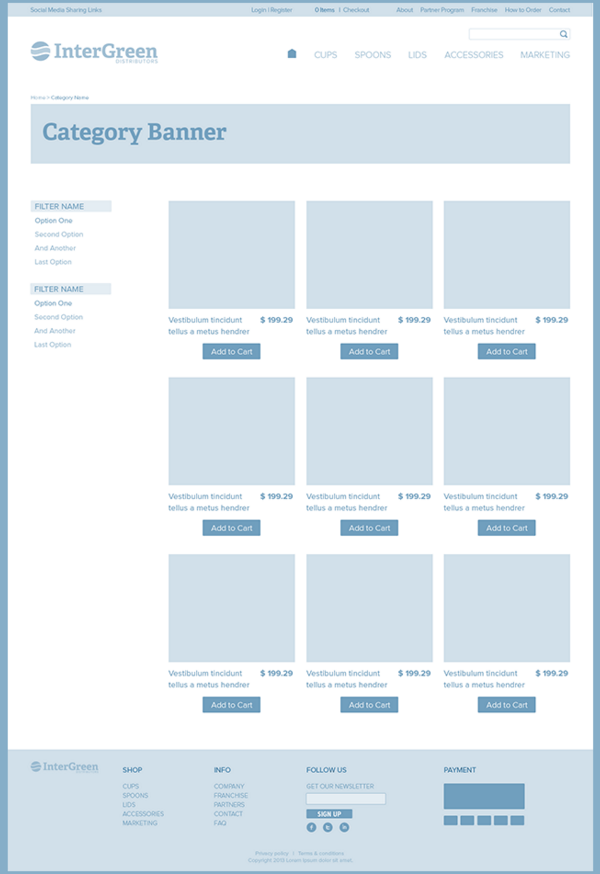
layout이란 웹사이트를 구성하는 요소들을 배치할 공간을 분할하고 정렬하는 것이다. 공간을 분할할 때는 먼저 행을 구분한 후, 행 내부 요소를 분리하는 것이 일반적이다.
아래 예제는 2 column layout의 일반적인 골격이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<header>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>...</li>
<li>...</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<div id="content-wrap">
<aside>
<ul>
<li>...</li>
<li>...</li>
</ul>
</aside>
<section>
<article>...</article>
<article>...</article>
</section>
</div>
<footer></footer>
</div>
</body>
</html>
1. Header & Navigation Bar
대부분의 웹사이트는 Navigation Bar를 가지고 있다. Navigation Bar는 웹사이트의 필수 구성 요소라고 할 수 있을 것이다.
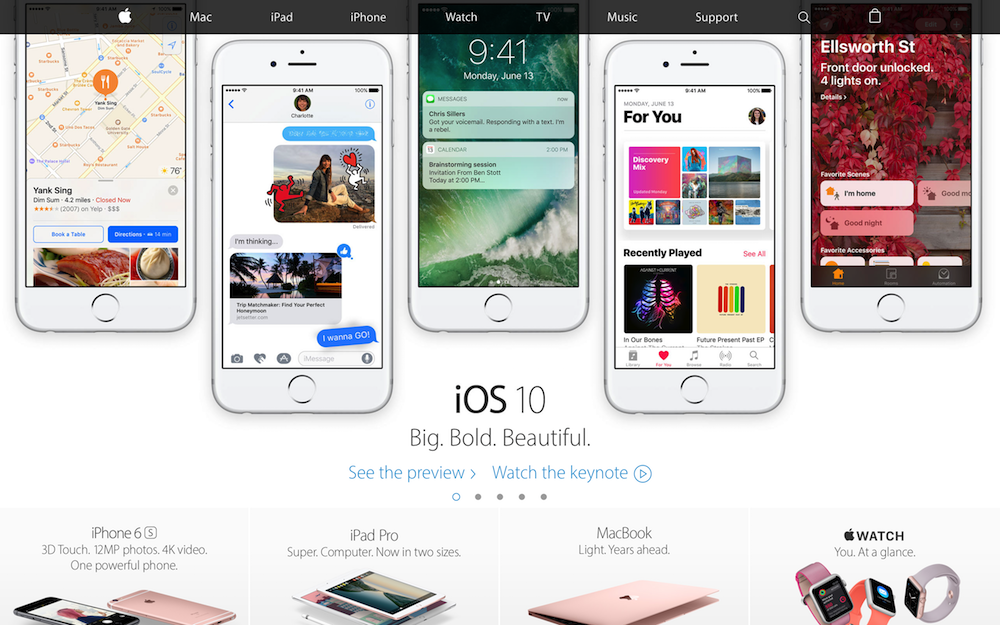 apple.com
apple.com
Navigation Bar는 기본적으로 링크들의 리스트이다. 따라서 ul, li tag를 이용하여 작성하는 것이 일반적이다.
다음은 최소한의 Reset CSS를 추가한 링크들의 리스트이다. 주의할 점은 직관적인 box model을 위해 box-sizing: border-box;을 사용했다는 것이다.
실제 웹사이트를 구축할 시에는 Reset CSS를 좀 더 정교하게 초기화할 필요가 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* Simple Reset CSS */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
color: #58666e;
background-color: #f0f3f4;
}
li {
list-style: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<header>
<a class="logo" href="#home">
<img src="https://poiemaweb.com/img/logo.png" height="36px">
</a>
<nav>
<ul class="nav-items">
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
</div>
</body>
</html>
header 요소에 화면폭 만큼의 width와 고정 height를 지정한다. background-color와 box-shadow 효과를 추가한다.
header {
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
z-index: 2000;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 2px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05), 0 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
}
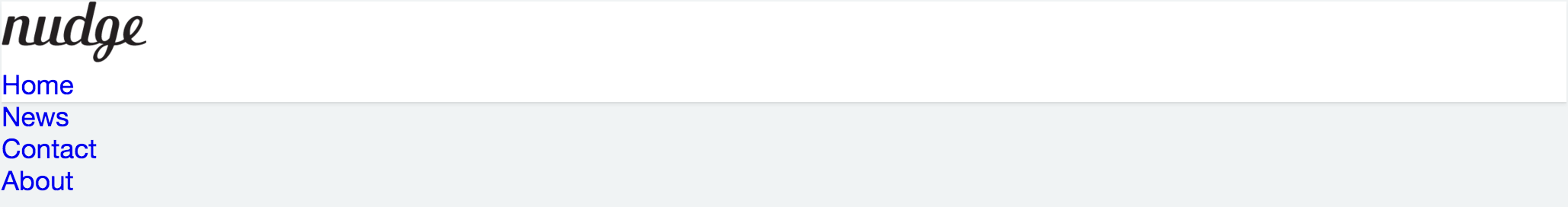
이제 float 프로퍼티를 이용하여 Navigation bar를 우측정렬한다.
nav {
float: right;
}

아래의 logo image를 수직으로 중앙 정렬한다.
<a class="logo" href="#home"><img src="https://poiemaweb.com/img/logo.png" height="36px"></a>
logo image를 포함하는 a tag(.logo)의 height를 logo image와 같은 height인 36px로 지정하고 상하 margin을 12px씩 부여하면 logo 요소의 높이는 60px이 되고 header의 height와 같아져 이미지는 수직 중앙 정렬된다.
a tag는 inline 요소이므로 margin을 정의하기 위해서 display: inline-block;을 설정한다. 또한 img tag에 부여한 height 어트리뷰트를 css로 옮긴다.
.logo {
display: inline-block;
height: 36px;
margin: 12px 0 12px 25px;
}
.logo > img { height: 36px; }

수직 정렬되어 있는 Navigation bar를 수평 정렬한다. block 요소인 li에 display: inline-block;를 설정하여 inline 요소와 같이 가로로 정렬케 한다.
.nav-items > li {
display: inline-block;
}

수평 정렬된 Navigation bar 수직 중앙 정렬한다. line-height: 60px;으로 텍스트의 높이를 header의 height와 동일하게 60px로 고정시킨다. 그리고 텍스트 간 적당한 간격 유지를 위해 padding을 정의한다.
.nav-items > li > a {
line-height: 60px;
padding: 0 30px;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
}

마우스가 Navigation bar 위에 올라오면 Navigation item의 텍스트 색상이 변경되도록 한다.
.nav-items > li > a:hover {
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.8);
}
아래는 완성된 Navigation bar의 예제 코드이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* Simple Reset CSS */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
color: #58666e;
background-color: #f0f3f4;
}
li {
list-style: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
header {
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
z-index: 2000;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 2px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05), 0 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
}
nav {
float: right;
}
.logo {
display: inline-block;
height: 36px;
margin: 12px 0 12px 25px;
}
.logo > img { height: 36px; }
.nav-items > li {
display: inline-block;
}
.nav-items > li > a {
line-height: 60px;
padding: 0 30px;
color: rgba(0,0,0,0.4);
}
.nav-items > li > a:hover {
color: rgba(0,0,0,0.8);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<header>
<a class="logo" href="#home">
<img src="https://poiemaweb.com/img/logo.png">
</a>
<nav>
<ul class="nav-items">
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2. Section & Aside
콘텐츠의 영역을 Section, 콘텐츠에 대한 Navigation item이나 부가 정보 영역을 Aside라 한다. Section 영역은 다시 article 영역으로 구분할 수 있다.
이 두개의 영역은 float 프로퍼티를 사용하여 수평 정렬하는 것이 일반적이다.
header 요소 뒤에 aside, section, article을 포함하는 content-wrap 요소를 정의한다.
<div id="content-wrap">
<aside>
<h1>Aside</h1>
<ul>
<li><a href="#" class="active">London</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Paris</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Tokyo</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Newyork</a></li>
</ul>
</aside>
<section>
<article id="london">
<h1>London</h1>
<p>...</p>
</article>
<article id="paris">
<h1>Paris</h1>
<p>...</p>
</article>
<article id="tokyo">
<h1>Tokyo</h1>
<p>...</p>
</article>
<article id="newyork">
<h1>Newyork</h1>
<p>...</p>
</article>
</section>
<!-- end of content-wrap -->
</div>
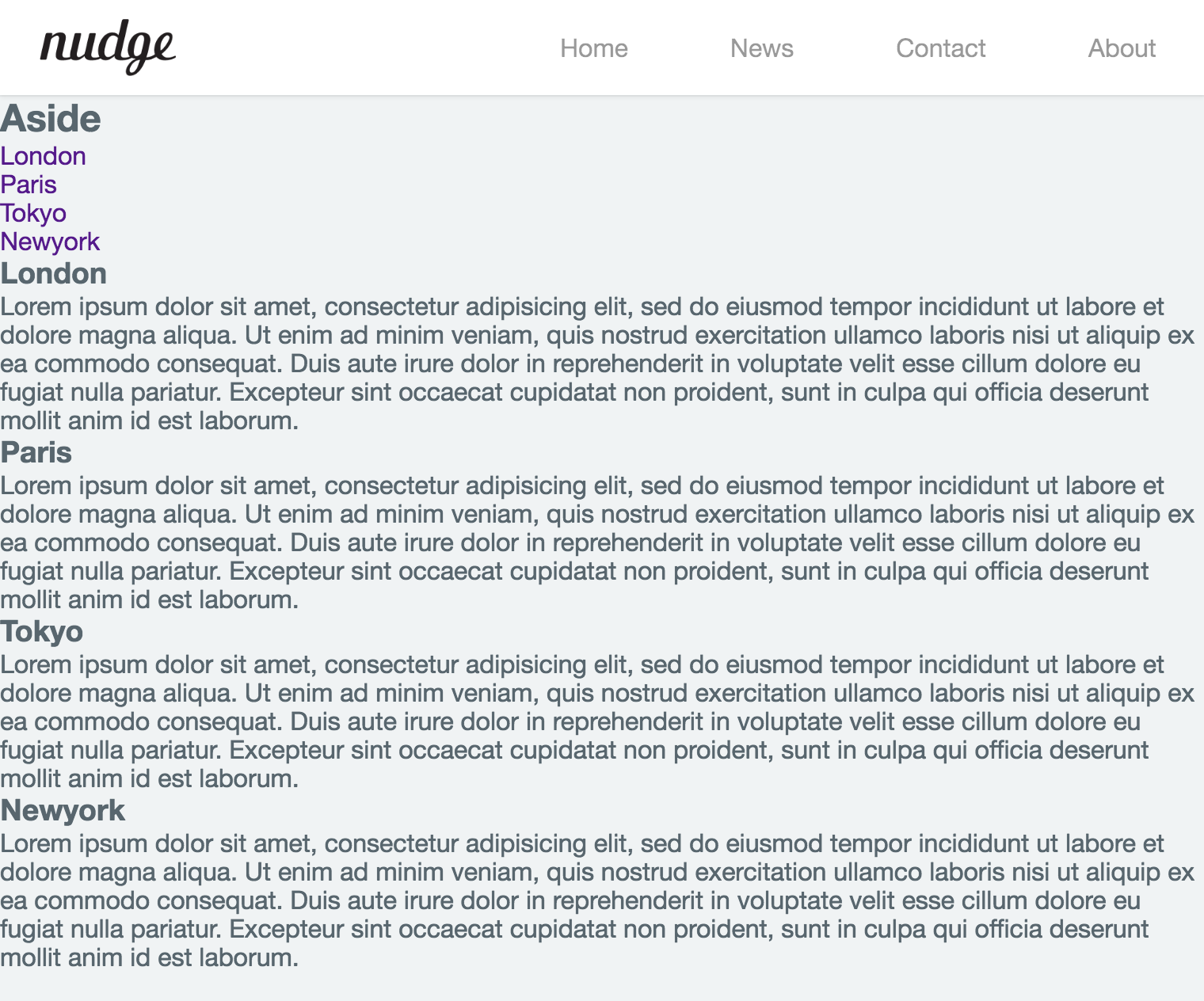
aside을 좌측정렬, section을 우측 정렬한다. 이때 float 프로퍼티 요소를 감싸는 wrap 요소에 clearfix을 부여하여 float 프로퍼티가 선언된 두개의 자식 요소를 포함하는 부모 요소의 높이가 정상적인 값을 가지지 못하는 문제를 해결해야 한다.
/* clearfix */
#content-wrap:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
aside {
float: left;
width: 20%;
}
section {
float: right;
width: 80%;
}
2개의 블록 영역이 수평 정렬되었고 wrap 요소도 정상적인 높이를 가지게 되었다. 그런데 아래 그림처럼 화면을 아래로 스크롤하면 header 영역도 따라 올라가 버려 navigation bar가 사라져 버리는 현상이 발생한다. navigation bar가 화면에 없으면 조작이 불편할 수 있으므로 navigation bar를 화면 상단에 고정시키도록 한다.
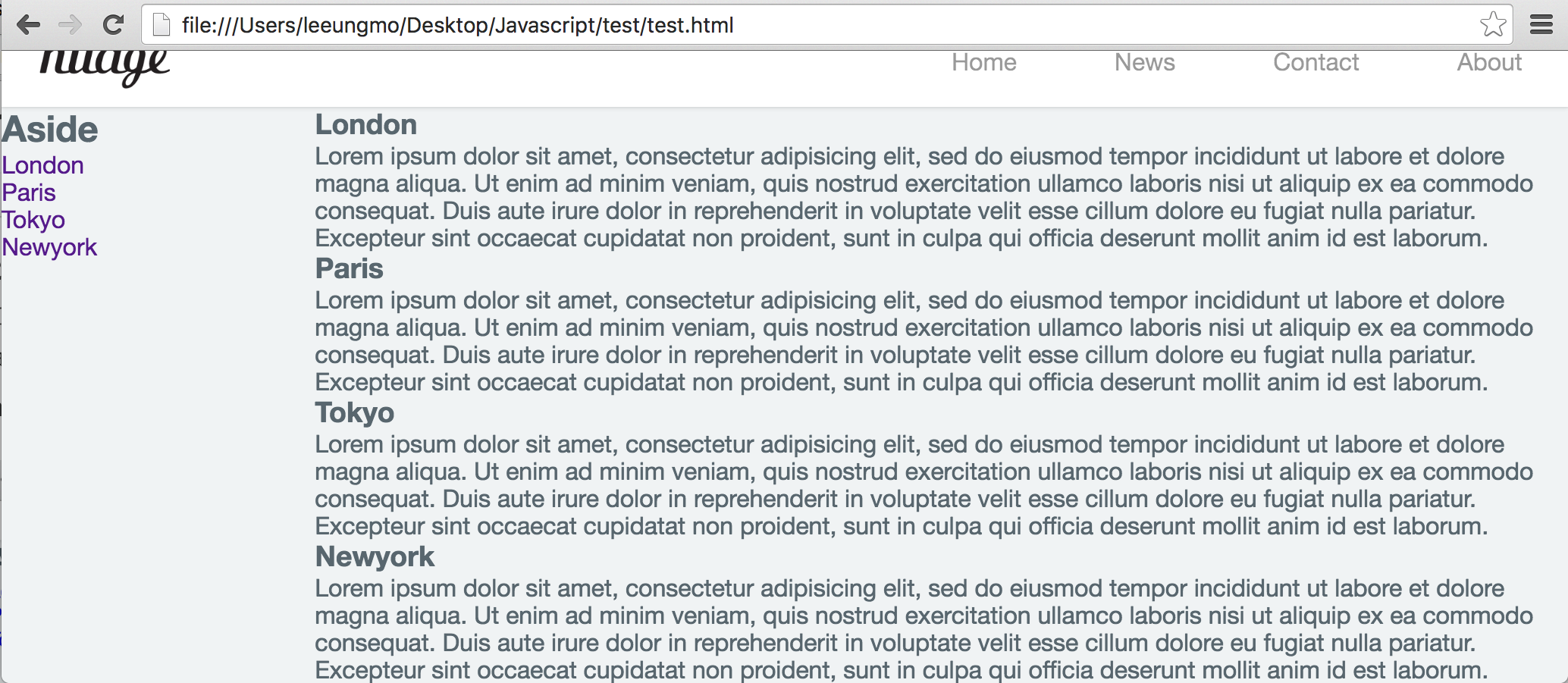
fixed 프로퍼티를 사용하여 header 요소를 상단에 고정시킨다.
fixed 프로퍼티은 부모 요소와 관계없이 브라우저의 viewport를 기준으로 좌표 프로퍼티(top, bottom, left, right)을 사용하여 위치를 이동시킨다. 스크롤이 되더라도 화면에서 사라지지 않고 항상 같은 곳에 위치한다.
header {
/* for sticky header */
position: fixed;
top: 0;
...
}
contents 영역 상단이 header 영역과 겹치므로 contents 영역을 header의 height 만큼 아래로 끌어 내린다.
#wrap {
/* margin-top = header height */
margin-top: 60p;
}
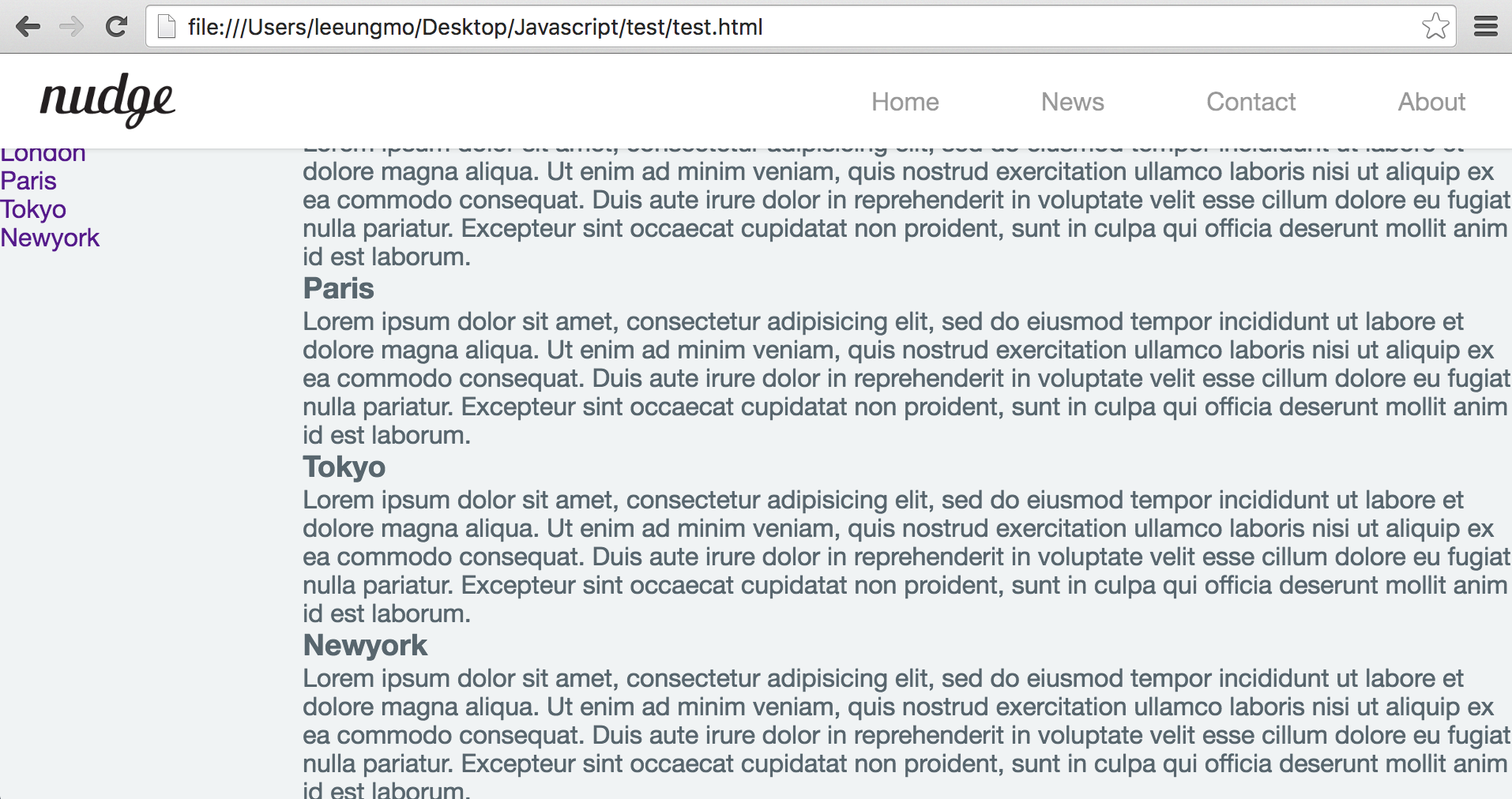
이제 header 영역은 고정되었다. 그런데 화면이 스크롤될 때 좌측 aside의 navigation이 사라지는 것은 마찬가지로 불편할 수 있다. aside 영역도 고정시키도록 하자.
float: left;를 삭제하고 header와 같이 position: fixed;를 추가한다. %로 지정했던 width도 고정폭으로 변경한다. 이때 section 영역의 % width도 삭제하여 aside 영역 만큼 우측으로 밀어서 나머지 영역을 모두 차지하도록 한다.
aside {
/* for fixed side bar */
position: fixed;
top: 60px;
bottom: 0;
width: 200px;
}
section {
float: right;
margin-left: 200px;
}

다음은 aside navigation의 style을 정리한다. 현재 active한 item을 컬러로 구분할 수 있게 하고 마우스 hover상태일 때도 컬러로 구분할 수 있게 한다. 또한 텍스트의 style도 정리한다.
aside {
/* for fixed side bar */
position: fixed;
top: 60px;
bottom: 0;
width: 200px;
padding-top: 25px;
background-color: #333;
}
/* aside navigation */
aside > ul {
width: 200px;
}
aside > ul > li > a {
display: block;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px 0 10px 20px;
}
aside > ul > li > a.active {
background-color: #4CAF50;
}
aside > ul > li > a:hover:not(.active) {
background-color: #555;
}
aside > h1 {
padding: 20px 0 20px 20px;
color: #fff;
}
/* Section */
section {
float: right;
/* aside width */
margin-left: 200px;
}
article {
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
background-color: white;
}
heading tag(h1)의 크기가 위치한 영역에 따라 다름에 주의하여야 한다. 즉, header내의 h1은 section내의 h1 보다 크다. 이것을 방지하기 위해서는 다음을 Rest CSS에 추가할 필요가 있다. 크기는 적당히 조절하면 된다. 다른 텍스트 태그의 style도 정리한다.
h1 { font-size: 1.8em; }
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p {
margin: 10px 5px;
}
자세한 사항은 MDN 참조하기 바란다.
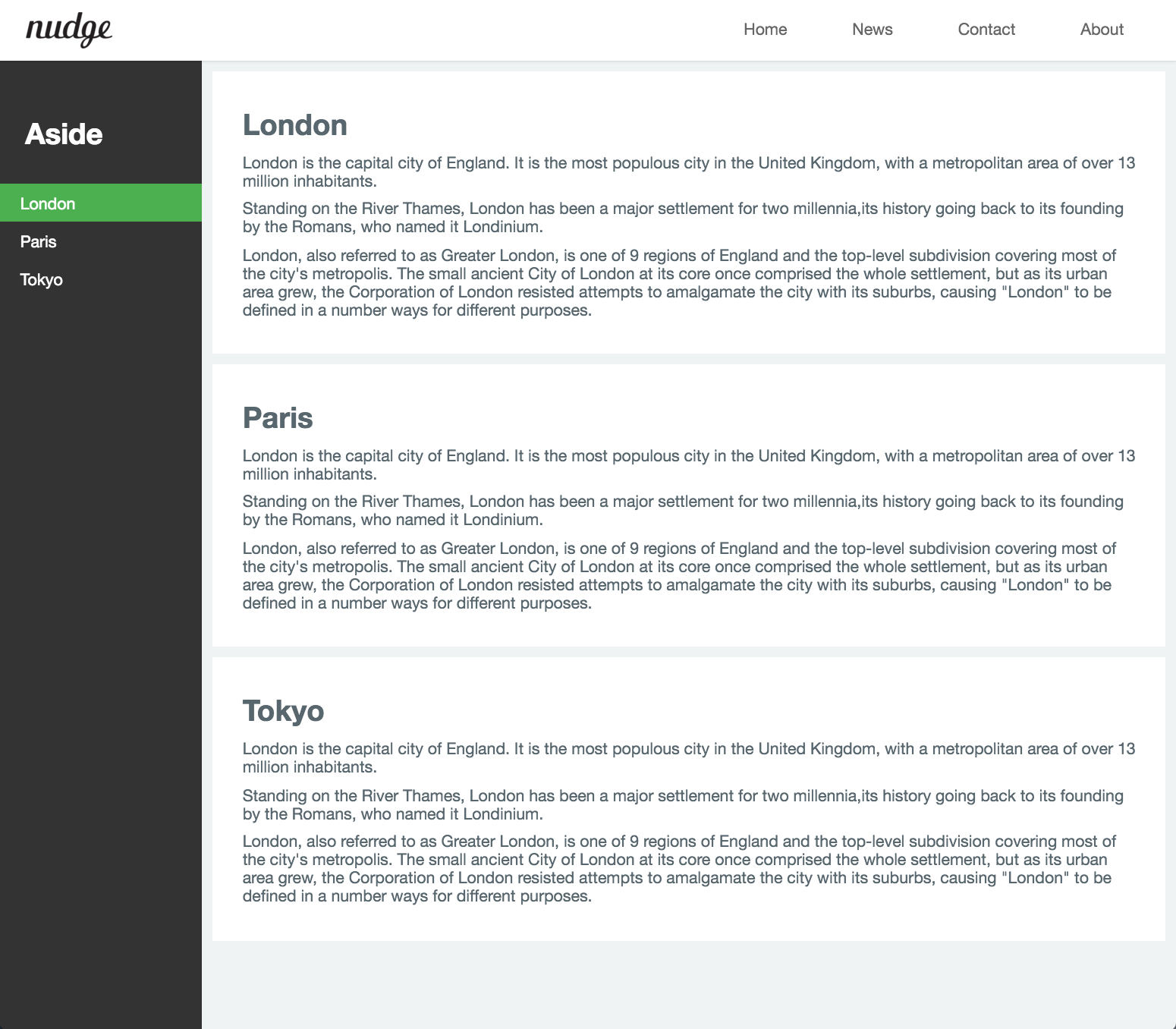
3. footer
content-wrap 영역 다음에 footer를 배치한다.
<footer>© Copyright 2016 ungmo2</footer>
footer도 고정되어 있을 필요가 있지만 본문을 가리는 것은 곤란하다. 따라서 fixed 프로퍼티를 설정해서는 않된다. fixed 프로퍼티는 스크롤이 되어도 언제나 그자리를 고수하기 때문이다.
footer는 absolute 프로퍼티를 설정한다. absolute를 사용하면 다른 요소가 먼저 위치를 점유하고 있어도 뒤로 밀리지 않고 덮어쓰게 된다. (이런 특성을 부유 또는 부유 객체라 한다)
footer의 style 정의는 다음과 같다.
footer {
/* footer를 aside위에 올리기 위해 사용(부유객체) */
position: absolute;
height: 60px;
width: 100%;
padding: 0 25px;
line-height: 60px;
color: #8a8c8f;
border-top: 1px solid #dee5e7;
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
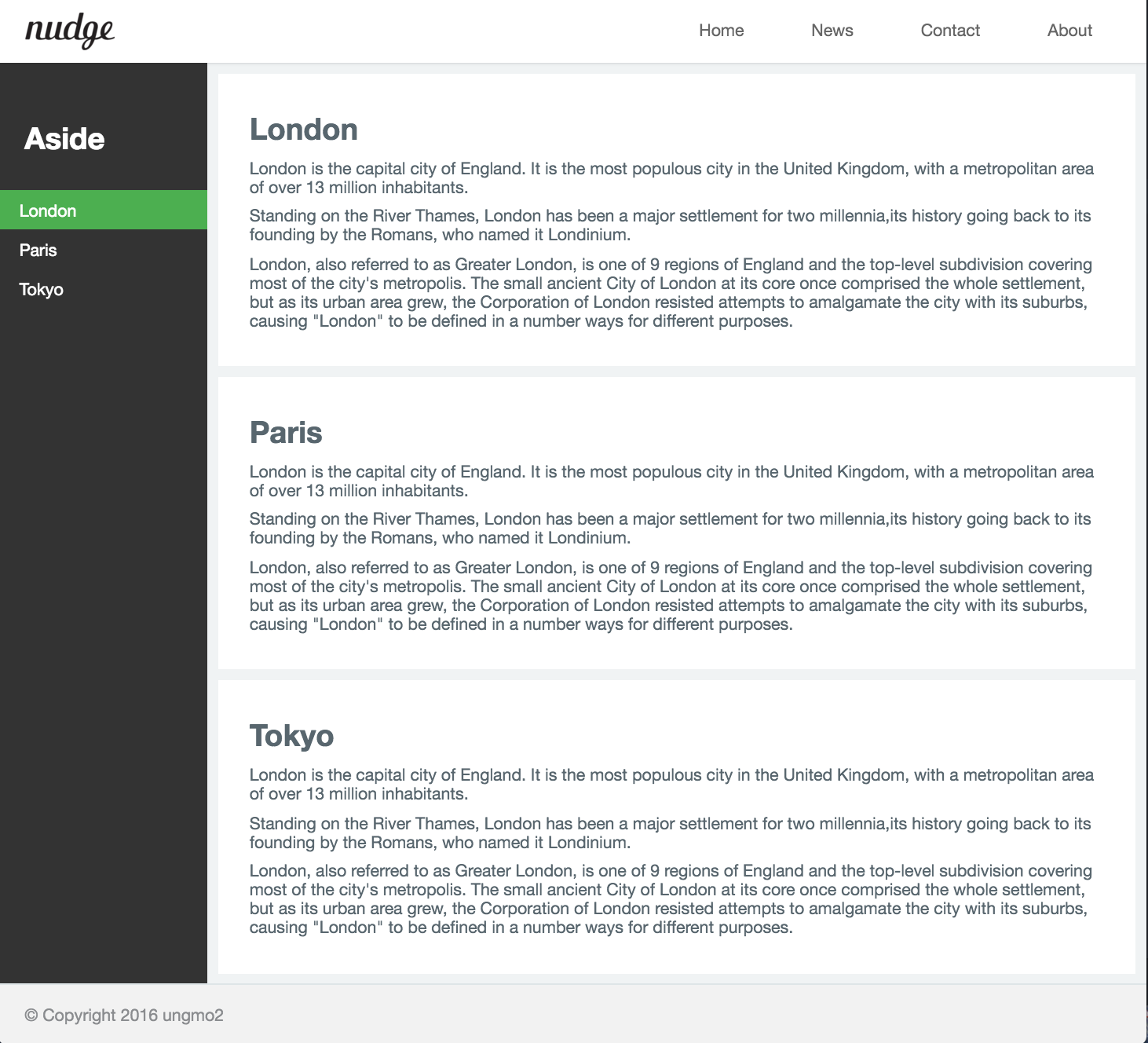
다음은 지금까지 작성한 예제의 전체 코드이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
/* Simple Reset CSS */
* {
margin: 0; padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
color: #58666e;
background-color: #f0f3f4;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-webkit-text-size-adjus: 100%; /* iphone font size 변경 방지 */
}
li { list-style: none; }
a { text-decoration: none; }
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p {
margin: 10px 5px;
}
h1 { font-size: 1.8em; }
#wrap {
width: 100%;
/* margin-top = header height */
margin-top: 60px;
}
/* Navigation bar */
header {
/* for sticky header */
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
z-index: 2000;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 2px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05), 0 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
}
.logo {
display: inline-block;
height: 36px;
margin: 12px 0 12px 25px;
}
.logo > img { height: 36px; }
nav {
float: right;
}
.nav-items {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.nav-items > li {
display: inline-block; /* 가로정렬 */
}
.nav-items > li > a {
/* for Vertical Centering */
line-height: 60px;
padding: 0 30px;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4);
}
.nav-items > li > a:hover {
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.8);
}
/* contents */
/* clearfix */
#content-wrap:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
aside {
/* for fixed side bar */
position: fixed;
top: 60px;
bottom: 0;
width: 200px; /* 너비 고정 */
padding-top: 25px;
background-color: #333;
}
/* aside navigation */
aside > ul {
width: 200px;
}
aside > ul > li > a {
display: block;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px 0 10px 20px;
}
aside > ul > li > a.active {
background-color: #4CAF50;
}
aside > ul > li > a:hover:not(.active) {
background-color: #555;
}
aside > h1 {
padding: 20px 0 20px 20px;
color: #fff;
}
/* Section */
section {
float: right;
/* aside width */
margin-left: 200px;
}
article {
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
background-color: white;
}
/* footer */
footer {
/* footer를 aside위에 올리기 위해 사용(부유객체) */
position: absolute;
height: 60px;
width: 100%;
padding: 0 25px;
line-height: 60px;
color: #8a8c8f;
border-top: 1px solid #dee5e7;
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<header>
<a class="logo" href="#home"><img src="https://poiemaweb.com/img/logo.png"></a>
<nav>
<ul class="nav-items">
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<div id="content-wrap">
<aside>
<h1>Aside</h1>
<ul>
<li><a href="#" class="active">London</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Paris</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Tokyo</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Newyork</a></li>
</ul>
</aside>
<section>
<article id="london">
<h1>London</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London, also referred to as Greater London, is one of 9 regions of England and the top-level subdivision covering most of the city's metropolis. The small ancient City of London at its core once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban area grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the city with its suburbs, causing "London" to be defined in a number ways for different purposes.</p>
</article>
<article id="paris">
<h1>Paris</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London, also referred to as Greater London, is one of 9 regions of England and the top-level subdivision covering most of the city's metropolis. The small ancient City of London at its core once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban area grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the city with its suburbs, causing "London" to be defined in a number ways for different purposes.</p>
</article>
<article id="tokyo">
<h1>Tokyo</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London, also referred to as Greater London, is one of 9 regions of England and the top-level subdivision covering most of the city's metropolis. The small ancient City of London at its core once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban area grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the city with its suburbs, causing "London" to be defined in a number ways for different purposes.</p>
</article>
<article id="newyork">
<h1>Newyork</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p>
<p>Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London, also referred to as Greater London, is one of 9 regions of England and the top-level subdivision covering most of the city's metropolis. The small ancient City of London at its core once comprised the whole settlement, but as its urban area grew, the Corporation of London resisted attempts to amalgamate the city with its suburbs, causing "London" to be defined in a number ways for different purposes.</p>
</article>
</section>
<!-- end of content-wrap -->
</div>
<footer>© Copyright 2016 ungmo2</footer>
<!-- end of wrap -->
</div>
</body>
</html>
사실 위의 예제에는 몇가지 문제가 숨겨져 있다. 그 문제를 해결할 열쇠는 바로 Responsive Web Design이다.
