- 1. 전체 셀렉터 (Universal Selector)
- 2. 태그 셀렉터 (Type Selector)
- 3. ID 셀렉터 (ID Selector)
- 4. 클래스 셀렉터 (Class Selector)
- 5. 어트리뷰트 셀렉터 (Attribute Selector)
- 6. 복합 셀렉터 (Combinator)
- 7. 가상 클래스 셀렉터 (Pseudo-Class Selector)
- 8. 가상 요소 셀렉터 (Pseudo-Element Selector)
- Reference
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)는 HTML 요소(Element)의 style(design, layout etc)을 정의한다. 그리하려면 HTML이 존재하여야 하고 또한 style을 적용하고자하는 HTML 요소를 특정할 필요가 있다.
이러한 목적으로 사용되는 것이 셀렉터(Selector)이다. 즉, style을 적용하고자하는 HTML 요소를 셀렉터로 특정하고 선택된 요소에 스타일을 정의하는 것이다.

CSS Rule Set
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 { color: red; }
p { color: blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This paragraph is styled with CSS.</p>
</body>
</html>
복수개의 셀렉터를 연속하여 지정할 수 있으며 쉼표( , )로 구분한다.
h1, p { color: red; }
1. 전체 셀렉터 (Universal Selector)
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| * | HTML 문서 내의 모든 요소를 선택한다. html 요소를 포함한 모든 요소가 선택된다. (head 요소도 포함된다) |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* 모든 요소를 선택 */
* { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div>
<p>paragraph 1</p>
<p>paragraph 2</p>
</div>
<p>paragraph 3</p>
</body>
</html>
2. 태그 셀렉터 (Type Selector)
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 태그명 | 지정된 태그명을 가지는 요소를 선택한다. |
지정된 태그명을 가지는 요소를 선택한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* 모든 p 태그 요소를 선택 */
p { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div>
<p>paragraph 1</p>
<p>paragraph 2</p>
</div>
<p>paragraph 3</p>
</body>
</html>
3. ID 셀렉터 (ID Selector)
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| #id 어트리뷰트 값 | id 어트리뷰트 값을 지정하여 일치하는 요소를 선택한다. id 어트리뷰트 값은 중복될 수 없는 유일한 값이다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* id 어트리뷰트 값이 p1인 요소를 선택 */
#p1 { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div class="container">
<p id="p1">paragraph 1</p>
<p id="p2">paragraph 2</p>
</div>
<p>paragraph 3</p>
</body>
</html>
4. 클래스 셀렉터 (Class Selector)
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| .class 어트리뷰트 값 | class 어트리뷰트 값을 지정하여 일치하는 요소를 선택한다. class 어트리뷰트 값은 중복될 수 있다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* class 어트리뷰트 값이 container인 모든 요소를 선택 */
/* color 어트리뷰트는 자식 요소에 상속된다. */
.container { color: red; }
/* not supported in IE */
#p2 { color: initial; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div class="container">
<p id="p1">paragraph 1</p>
<p id="p2">paragraph 2</p>
</div>
<p>paragraph 3</p>
</body>
</html>
HTML 요소에 class 어트리뷰트 값은 공백으로 구분하여 여러 개 지정할 수 있다. 아래와 같이 클래스 셀렉터를 사용하여 미리 스타일을 정의해 두고, HTML 요소는 이미 정의되어 있는 클래스를 지정하는 것으로 필요한 스타일을 지정할 수 있다. 이것은 재사용의 측면에서 유용하다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* class 어트리뷰트 값이 text-center인 모든 요소를 선택 */
.text-center { text-align: center; }
/* class 어트리뷰트 값이 text-large인 모든 요소를 선택 */
.text-large { font-size: 200%; }
/* class 어트리뷰트 값이 text-red인 모든 요소를 선택 */
.text-red { color: red; }
/* class 어트리뷰트 값이 text-blue인 모든 요소를 선택 */
.text-blue { color: blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="text-center">Center</p>
<p class="text-large text-red">Large Red</p>
<p class="text-center text-large text-blue">Center Large Blue</p>
</body>
</html>
5. 어트리뷰트 셀렉터 (Attribute Selector)
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트] | 지정된 어트리뷰트를 갖는 모든 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소 중에 href 어트리뷰트를 갖는 모든 요소 */
a[href] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.poiemaweb.com">poiemaweb.com</a><br>
<a href="http://www.google.com" target="_blank">google.com</a><br>
<a href="http://www.naver.com" target="_top">naver.com</a>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트를 가지며 지정된 값과 어트리뷰트의 값이 일치하는 모든 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소 중에 target 어트리뷰트의 값이 "_blank"인 모든 요소 */
a[target="_blank"] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.poiemaweb.com">poiemaweb.com</a><br>
<a href="http://www.google.com" target="_blank">google.com</a><br>
<a href="http://www.naver.com" target="_top">naver.com</a>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트~=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트의 값이 지정된 값을 (공백으로 분리된) 단어로 포함하는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* h1 요소 중에 title 어트리뷰트 값에 "first"를 단어로 포함하는 요소 */
h1[title~="first"] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 title="heading first">Heading first</h1>
<h1 title="heading-first">Heading-first</h1>
<h1 title="heading second">Heading second</h1>
<h1 title="heading third">Heading third</h1>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트|=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트의 값과 일치하거나 지정 어트리뷰트 값 뒤 연이은 하이픈(“값-“)으로 시작하는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소 중에 lang 어트리뷰트 값이 "en"과 일치하거나 "en-"로 시작하는 요소 */
p[lang|="en"] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p lang="en">Hello!</p>
<p lang="en-us">Hi!</p>
<p lang="en-gb">Ello!</p>
<p lang="us">Hi!</p>
<p lang="no">Hei!</p>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트^=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트 값으로 시작하는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소 중에 href 어트리뷰트 값이 "https://"로 시작하는 요소 */
a[href^="https://"] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.test.com">https://www.test.com</a><br>
<a href="http://www.test.com">http://www.test.com</a>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트$=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트 값으로 끝나는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소 중에 href 어트리뷰트 값이 ".html"로 끝나는 요소 */
a[href$=".html"] { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="test.html">test.html</a><br>
<a href="test.jsp">test.jsp</a>
</body>
</html>
| 패턴 | Description |
|---|---|
| 셀렉터[어트리뷰트*=”값”] | 지정된 어트리뷰트 값을 포함하는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* div 요소 중에서 class 어트리뷰트 값에 "test"를 포함하는 요소 */
div[class*="test"] { color: red; }
/* div 요소 중에서 class 어트리뷰트 값에 "test"를 단어로 포함하는 요소 */
div[class~="test"] { background-color: yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="first_test">The first div element.</div>
<div class="second">The second div element.</div>
<div class="test">The third div element.</div>
<p class="test">This is some text in a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
6. 복합 셀렉터 (Combinator)
6.1 후손 셀렉터 (Descendant Combinator)
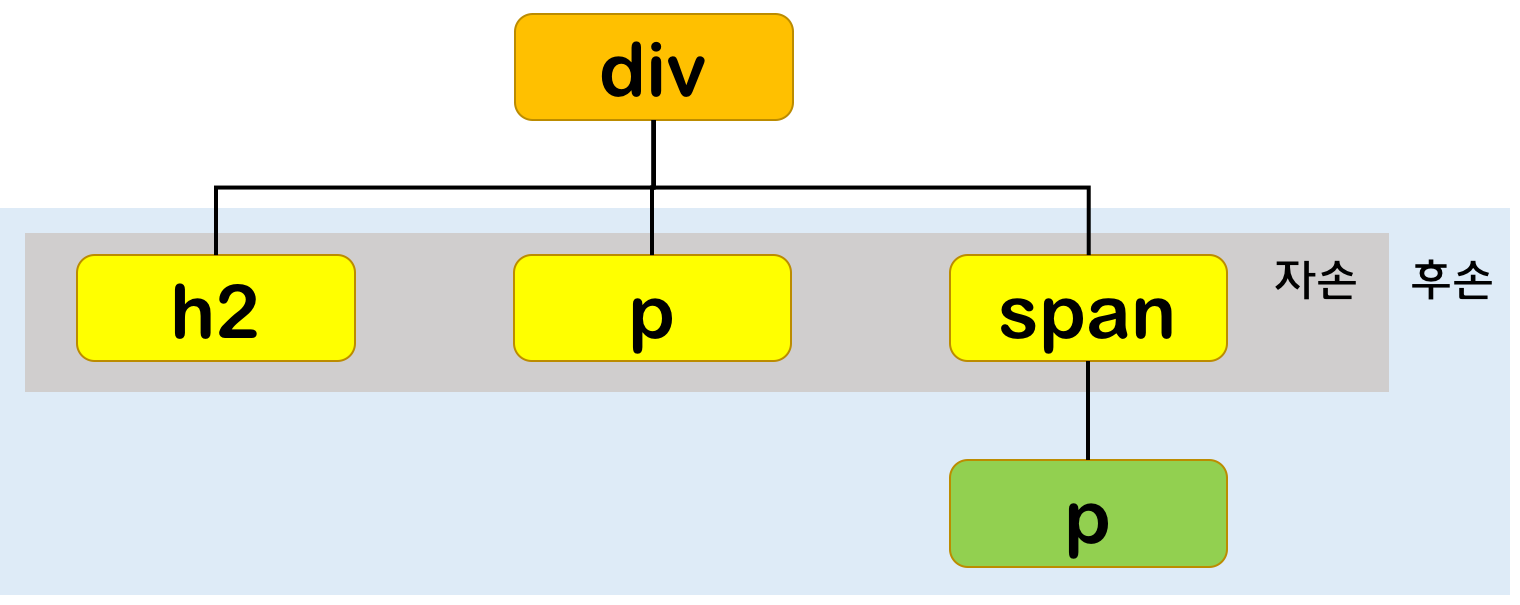
자신의 1 level 상위에 속하는 요소를 부모 요소, 1 level 하위에 속하는 요소를 자손 요소(자식 요소)라한다.
자신보다 n level 하위에 속하는 요소는 후손 요소(하위 요소)라 한다.
후손 셀렉터는 셀렉터A의 모든 후손(하위) 요소 중 셀렉터B와 일치하는 요소를 선택한다.
셀렉터A 셀렉터B
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* div 요소의 후손요소 중 p 요소 */
div p { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div>
<p>paragraph 1</p>
<p>paragraph 2</p>
<span><p>paragraph 3</p></span>
</div>
<p>paragraph 4</p>
</body>
</html>
6.2 자식 셀렉터 (Child Combinator)
자손 셀렉터는 셀렉터A의 모든 자식 요소 중 셀렉터B와 일치하는 요소를 선택한다.
셀렉터A > 셀렉터B
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* div 요소의 자식요소 중 p 요소 */
div > p { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<div>
<p>paragraph 1</p>
<p>paragraph 2</p>
<span><p>paragraph 3</p></span>
</div>
<p>paragraph 4</p>
</body>
</html>
6.3 형제(동위) 셀렉터 (Sibling Combinator)
형제(동위) 셀렉터는 형제 관계(동위 관계)에서 뒤에 위치하는 요소를 선택할 때 사용한다.
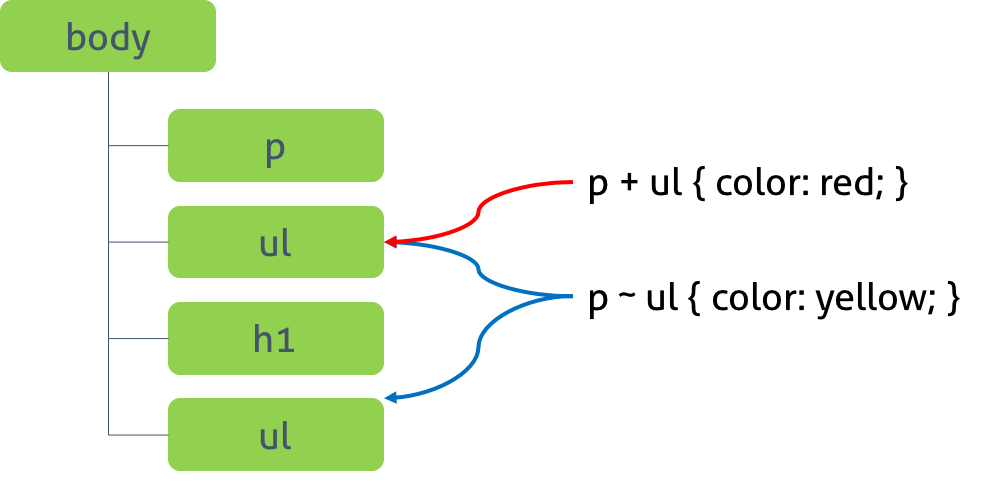
6.3.1 인접 형제 셀렉터(Adjacent Sibling Combinator)
셀렉터A의 형제 요소 중 셀렉터A 바로 뒤에 위치하는 셀렉터B 요소를 선택한다. A와 B 사이에 다른 요소가 존재하면 선택되지 않는다.
셀렉터A + 셀렉터B
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소의 형제 요소 중에 p 요소 바로 뒤에 위치하는 ul 요소를 선택한다. */
p + ul { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>A div element.</div>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
<p>The first paragraph.</p>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
<h2>Another list</h2>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
6.3.2 일반 형제 셀렉터(General Sibling Combinator)
셀렉터A의 형제 요소 중 셀렉터A 뒤에 위치하는 셀렉터B 요소를 모두 선택한다.
셀렉터A ~ 셀렉터B
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소의 형제 요소 중에 p 요소 뒤에 위치하는 ul 요소를 모두 선택한다.*/
p ~ ul { color: red; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>A div element.</div>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
<p>The first paragraph.</p>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
<h2>Another list</h2>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
7. 가상 클래스 셀렉터 (Pseudo-Class Selector)
가상 클래스는 요소의 특정 상태에 따라 스타일을 정의할 때 사용된다. 특정 상태란 예를 들어 다음과 같다.
-
마우스가 올라와 있을때
-
링크를 방문했을 때와 아직 방문하지 않았을 때
-
포커스가 들어와 있을 때
이러한 특정 상태에는 원래 클래스가 존재하지 않지만 가상 클래스를 임의로 지정하여 선택하는 방법이다.
가상 클래스는 마침표(.) 대신 콜론(:)을 사용한다. CSS 표준에 의해 미리 정의된 이름이 있기 때문에 임의의 이름을 사용할 수 없다.
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
다음은 div 요소가 hover 상태일 때(마우스가 올라와 있을 때) background-color를 red로 지정하는 예이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소가 hover 상태일 때 */
a:hover { background-color: red; }
/* input 요소가 focus 상태일 때 */
input:focus { background-color: yellow; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">Hover me</a><br><br>
<input type="text" placeholder="focus me">
</body>
</html>
7.1 링크 셀렉터(Link pseudo-classes), 동적 셀렉터(User action pseudo-classes)
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :link | 셀렉터가 방문하지 않은 링크일 때 |
| :visited | 셀렉터가 방문한 링크일 때 |
| :hover | 셀렉터에 마우스가 올라와 있을 때 |
| :active | 셀렉터가 클릭된 상태일 때 |
| :focus | 셀렉터에 포커스가 들어와 있을 때 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* a 요소가 방문하지 않은 링크일 때 */
a:link { color: orange; }
/* a 요소가 방문한 링크일 때 */
a:visited { color: green; }
/* a 요소에 마우스가 올라와 있을 때 */
a:hover { font-weight: bold; }
/* a 요소가 클릭된 상태일 때 */
a:active { color: blue; }
/* text input 요소와 password input 요소에 포커스가 들어와 있을 때 */
input[type=text]:focus,
input[type=password]:focus {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#" target="_blank">This is a link</a><br>
<input type="text" value="I'll be red when focused"><br>
<input type="password" value="I'll be red when focused">
</body>
</html>
7.2 UI 요소 상태 셀렉터(UI element states pseudo-classes)
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :checked | 셀렉터가 체크 상태일 때 |
| :enabled | 셀렉터가 사용 가능한 상태일 때 |
| :disabled | 셀렉터가 사용 불가능한 상태일 때 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* input 요소가 사용 가능한 상태일 때,
input 요소 바로 뒤에 위치하는 인접 형제 span 요소를 선택 */
input:enabled + span {
color: blue;
}
/* input 요소가 사용 불가능한 상태일 때,
input 요소 바로 뒤에 위치하는 인접 형제 span 요소를 선택 */
input:disabled + span {
color: gray;
text-decoration: line-through;
}
/* input 요소가 체크 상태일 때,
input 요소 바로 뒤에 위치하는 인접 형제 span 요소를 선택 */
input:checked + span {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input type="radio" checked="checked" value="male" name="gender"> <span>Male</span><br>
<input type="radio" value="female" name="gender"> <span>Female</span><br>
<input type="radio" value="neuter" name="gender" disabled> <span>Neuter</span><hr>
<input type="checkbox" checked="checked" value="bicycle"> <span>I have a bicycle</span><br>
<input type="checkbox" value="car"> <span>I have a car</span><br>
<input type="checkbox" value="motorcycle" disabled> <span>I have a motorcycle</span>
</body>
</html>
7.3 구조 가상 클래스 셀렉터(Structural pseudo-classes)
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :first-child | 셀렉터에 해당하는 모든 요소 중 첫번째 자식인 요소를 선택한다. |
| :last-child | 셀렉터에 해당하는 모든 요소 중 마지막 자식인 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소 중에서 첫번째 자식을 선택 */
p:first-child { color: red; }
/* p 요소 중에서 마지막 자식을 선택 */
/* body 요소의 두번째 p 요소는 마지막 자식 요소가 아니다.
body 요소의 마지막 자식 요소는 div 요소이다. */
p:last-child { color: blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This paragraph is the first child of its parent (body).</p>
<h1>Welcome to My Homepage</h1>
<p>This paragraph is not the first child of its parent.</p>
<div>
<p>This paragraph is the first child of its parent (div).</p>
<p>This paragraph is not the first child of its parent.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :nth-child(n) | 셀렉터에 해당하는 모든 요소 중 앞에서 n번째 자식인 요소를 선택한다. |
| :nth-last-child(n) | 셀렉터에 해당하는 모든 요소 중 뒤에서 n번째 자식인 요소를 선택한다. |
n은 0부터 시작하는 정수이다.
| n | 2n+1 | 2n-1 | 3n-2 | 3n+1 | -n+5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | -1 | -2 | 1 | 5 |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| 3 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 2 |
| 4 | 9 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 1 |
| 5 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 16 | 0 |
0과 음수는 생략되기 때문에 2n+1과 2n-1, 3n-2와 3n+1은 결과적으로 같은 수열을 생성한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 짝수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(2n) { color: orange; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 홀수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(2n+1) { color: green; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 첫번쨰 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:first-child { color: red; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 마지막 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:last-child { color: blue; }
/* ol 요소의 자식 요소인 li 요소 중에서 4번째 요소 요소만을 선택 */
ol > li:nth-child(4) { background: brown; }
/* ul 요소의 모든 자식 요소 중에서 뒤에서부터 시작하여 홀수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ul > :nth-last-child(2n+1) { color: red; }
/* ul 요소의 모든 자식 요소 중에서 뒤에서부터 시작하여 짝수번째 요소만을 선택 */
ul > :nth-last-child(2n) { color: blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>Espresso</li>
<li>Americano</li>
<li>Caffe Latte</li>
<li>Caffe Mocha</li>
<li>Caramel Latte</li>
<li>Cappuccino</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>Espresso</li>
<li>Americano</li>
<li>Caffe Latte</li>
<li>Caffe Mocha</li>
<li>Caramel Latte</li>
<li>Cappuccino</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :first-of-type | 셀렉터에 해당하는 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 첫번째 등장하는 요소를 선택한다. |
| :last-of-type | 셀렉터에 해당하는 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 마지막에 등장하는 요소를 선택한다. |
| :nth-of-type(n) | 셀렉터에 해당하는 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 앞에서 n번째에 등장하는 요소를 선택한다. |
| :nth-last-of-type(n) | 셀렉터에 해당하는 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 뒤에서 n번째에 등장하는 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 첫번째 등장하는 p 요소 */
p:first-of-type { color: red; }
/* p 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 마지막 등장하는 p 요소 */
p:last-of-type { color: blue; }
/* p 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 앞에서 2번째에 등장하는 p 요소 */
p:nth-of-type(2) { color: green; }
/* p 요소의 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 뒤에서 2번째에 등장하는 p 요소 */
p:nth-last-of-type(2) { color: orange;}
/* p 요소 중에서 첫번째 자식을 선택 */
p:first-child { background: brown;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>The first paragraph.</p>
<p>The second paragraph.</p>
<p>The third paragraph.</p>
<p>The fourth paragraph.</p>
<div>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>The first paragraph.</p>
<p>The second paragraph.</p>
<p>The third paragraph.</p>
<p>The fourth paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7.4 부정 셀렉터(Negation pseudo-class)
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :not(셀렉터) | 셀렉터에 해당하지 않는 모든 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* input 요소 중에서 type 어트리뷰트의 값이 password가 아닌 요소를 선택 */
input:not([type=password]) {
background: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" value="Text input">
<input type="email" value="email input">
<input type="password" value="Password input">
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
div {
float: left;
width: 32%;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
/* margin-bottom: 2%; */
color: #fff;
font-size: 3em;
line-height: 200px;
text-align: center;
}
/* div 요소 중에서 1, 4, 7...번째 등장하는 요소가 아닌 요소만을 선택 */
/* 1, 4, 7... : 공차가 3인 등차수열 */
div:not(:nth-of-type(3n+1)) {
margin-left: 2%;
}
/* div 요소 중에서 4번째 이후 등장하는 요소가 아닌 요소만을 선택 */
div:not(:nth-of-type(n+4)) {
margin-bottom: 2%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
<div>6</div>
</body>
</html>
7.5 정합성 체크 셀렉터(validity pseudo-class)
| pseudo-class | Description |
|---|---|
| :valid(셀렉터) | 정합성 검증이 성공한 input 요소 또는 form 요소를 선택한다. |
| :invalid(셀렉터) | 정합성 검증이 실패한 input 요소 또는 form 요소를 선택한다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input[type="text"]:valid {
background-color: greenyellow;
}
input[type="text"]:invalid {
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<label>입력값이 반드시 필요
<input type="text" required>
</label>
<br>
<label>특수문자를 포함하지 않는 4자리 문자 또는 숫자
<input type="text" value="ab1!"
pattern="[a-zA-Z0-9]{4}" required>
</label>
<br>
<label>핸드폰 번호 형식
<input type="text" value="010-1111-2222"
pattern="^\d{3}-\d{3,4}-\d{4}$" required>
</label>
</body>
</html>
8. 가상 요소 셀렉터 (Pseudo-Element Selector)
가상 요소는 요소의 특정 부분에 스타일을 적용하기 위하여 사용된다. 특정 부분이란 예를 들어 다음과 같다.
-
요소 콘텐츠의 첫글자 또는 첫줄
-
요소 콘텐츠의 앞 또는 뒤
가상 요소에는 두개의 콜론(::)을 사용한다. CSS 표준에 의해 미리 정의된 이름이 있기 때문에 임의의 이름을 사용할 수 없다.
selector::pseudo-element {
property:value;
}
| pseudo-element | Description |
|---|---|
| ::first-letter | 콘텐츠의 첫글자를 선택한다. |
| ::first-line | 콘텐츠의 첫줄을 선택한다. 블록 요소에만 적용할 수 있다. |
| ::after | 콘텐츠의 뒤에 위치하는 공간을 선택한다. 일반적으로 content 프로퍼티와 함께 사용된다. |
| ::before | 콘텐츠의 앞에 위치하는 공간을 선택한다. 일반적으로 content 프로퍼티와 함께 사용된다. |
| ::selection | 드래그한 콘텐츠를 선택한다. iOS Safari 등 일부 브라우저에서 동작 않는다. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* p 요소 콘텐츠의 첫글자를 선택 */
p::first-letter { font-size: 3em; }
/* p 요소 콘텐츠의 첫줄을 선택 */
p::first-line { color: red; }
/* h1 요소 콘텐츠의 앞 공간에 content 어트리뷰트 값을 삽입한다 */
h1::before {
content: " HTML!!! ";
color: blue;
}
/* h1 요소 콘텐츠의 뒷 공간에 content 어트리뷰트 값을 삽입한다 */
h1::after {
content: " CSS3!!!";
color: red;
}
/* 드래그한 콘텐츠를 선택한다 */
::selection {
color: red;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Explicabo illum sunt distinctio sed, tempore, repellat rerum et ea laborum voluptatum! Quisquam error fugiat debitis maiores officiis, tenetur ullam amet in!</p>
</body>
</html>
