자바스크립트는 동적 타입(dynamic typed) 언어이므로 변수에 어떤 값이 할당될 지 예측하기 어렵다. 아래 코드를 살펴보자.
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
위 코드를 작성한 개발자의 의도는 아마도 2개의 number 타입 인수를 전달받아 그 합계를 반환하려는 것으로 추측된다. 하지만 코드 상으로는 어떤 타입의 인수를 전달하여야 하는지, 어떤 타입의 값을 반환해야 하는지 명확하지 않다. 따라서 위 코드는 다음처럼 호출될 수 있다.
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
sum('x', 'y'); // 'xy'
위 코드는 자바스크립트 문법 상 어떠한 문제도 없으므로 자바스크립트 엔진은 아무런 이의 제기없이 위 코드를 실행할 것이다. 이러한 상황이 발생한 이유는 변수나 반환값의 타입을 사전에 지정하지 않는 자바스크립트의 동적 타이핑(Dynamic Typing)에 의한 것이다. 이와 같은 이유로 자바스크립트는 타입 체크가 필요하다.
function sum(a, b) {
// a와 b가 number 타입인지 체크
return a + b;
}
1. typeof
타입 연산자(Type Operator) typeof는 피연산자의 데이터 타입을 문자열로 반환한다.
typeof ''; // string
typeof 1; // number
typeof NaN; // number
typeof true; // boolean
typeof []; // object
typeof {}; // object
typeof new String(); // object
typeof new Date(); // object
typeof /test/gi; // object
typeof function () {}; // function
typeof undefined; // undefined
typeof null; // object (설계적 결함)
typeof undeclared; // undefined (설계적 결함)
그런데 typeof 연산자는 null과 배열의 경우 object, 함수의 경우 function를 반환하고, Date, RegExp, 사용자 정의 객체 등 거의 모든 객체의 경우, object를 반환한다. 따라서 typeof는 null을 제외한 원시 타입을 체크하는 데는 문제가 없지만 객체의 종류까지 구분하여 체크하려할 때는 사용하기는 곤란하다. 여러 종류의 객체(일반 객체, 배열, Date, RegExp, Function, DOM 요소 등)를 구분할 수 있는 타입 체크 기능을 만들어보자.
2. Object.prototype.toString
Object.prototype.toString 메소드는 객체를 나타내는 문자열을 반환한다.
var obj = new Object();
obj.toString(); // [object Object]
Function.prototype.call 메소드를 사용하면 모든 타입의 값의 타입을 알아낼 수 있다.
Object.prototype.toString.call(''); // [object String]
Object.prototype.toString.call(new String()); // [object String]
Object.prototype.toString.call(1); // [object Number]
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Number()); // [object Number]
Object.prototype.toString.call(NaN); // [object Number]
Object.prototype.toString.call(Infinity); // [object Number]
Object.prototype.toString.call(true); // [object Boolean]
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined); // [object Undefined]
Object.prototype.toString.call(); // [object Undefined]
Object.prototype.toString.call(null); // [object Null]
Object.prototype.toString.call([]); // [object Array]
Object.prototype.toString.call({}); // [object Object]
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date()); // [object Date]
Object.prototype.toString.call(Math); // [object Math]
Object.prototype.toString.call(/test/i); // [object RegExp]
Object.prototype.toString.call(function () {}); // [object Function]
Object.prototype.toString.call(document); // [object HTMLDocument]
Object.prototype.toString.call(argument); // [object Arguments]
Object.prototype.toString.call(undeclared); // ReferenceError
이것을 이용하여 타입을 반환하는 함수를 만들어보자.
function getType(target) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(target).slice(8, -1);
}
String.prototype.slice 메소드를 사용하여 Object.prototype.toString.call 메소드가 반환한 문자열에서 “[object”와 “]”를 제외하고 타입을 나타내는 문자열만을 추출하였다.
getType(''); // String
getType(1); // Number
getType(true); // Boolean
getType(undefined); // Undefined
getType(null); // Null
getType({}); // Object
getType([]); // Array
getType(/test/i); // RegExp
getType(Math); // Math
getType(new Date()); // Date
getType(function () {}); // Function
이제 앞에서 살펴본 sum 함수에 타입 체크 기능을 추가해 보자.
function sum(a, b) {
// a와 b가 number 타입인지 체크
if (getType(a) !== 'Number' || getType(b) !== 'Number') {
throw new TypeError('파라미터에 number 타입이 아닌 값이 할당되었습니다.');
}
return a + b;
}
console.log(sum(10, 20)); // 30
console.log(sum('10', 20)); // TypeError
타입별로 체크하는 기능을 만들려면 아래와 같이 함수를 작성한다.
function getType(target) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(target).slice(8, -1);
}
function isString(target) {
return getType(target) === 'String';
}
function isNumber(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Number';
}
function isBoolean(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Boolean';
}
function isNull(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Null';
}
function isUndefined(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Undefined';
}
function isObject(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Object';
}
function isArray(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Array';
}
function isDate(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Date';
}
function isRegExp(target) {
return getType(target) === 'RegExp';
}
function isFunction(target) {
return getType(target) === 'Function';
}
3. instanceof
이와 같이 Object.prototype.toString를 사용하여 객체의 종류(일반 객체, 배열, Date, RegExp, Function, DOM 요소 등)까지 식별할 수 있는 타입 체크 기능을 작성하였다.
그런데, 이 방법으로는 객체의 상속 관계까지 체크할 수는 없다. 아래의 예제를 살펴보자.
// HTMLElement를 상속받은 모든 DOM 요소에 css 프로퍼티를 추가하고 값을 할당한다.
function css(elem, prop, val) {
// type checking...
elem.style[prop] = val;
}
css({}, 'color', 'red');
// TypeError: Cannot set property 'color' of undefined
css 함수의 첫번째 매개변수에는 반드시 HTMLElement를 상속받은 모든 DOM 요소를 전달하여야 한다. 다시말해, css 함수의 첫번째 매개변수에는 HTMLDivElement, HTMLUListElement, HTMLLIElement, HTMLParagraphElement 등 모든 DOM 요소가 전달될 수 있다. 이를 일일이 체크할 수는 없기 때문에 HTMLElement를 상속받은 객체, 즉 DOM 요소인지 확인하여야 한다.
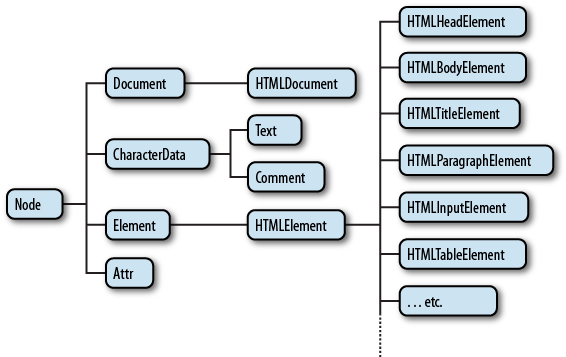
타입 연산자(Type Operator)에는 앞서 살펴본 typeof 이외에 instanceof를 제공한다. instanceof 연산자는 피연산자인 객체가 우항에 명시한 타입의 인스턴스인지 여부를 알려준다. 이때 타입이란 constructor를 말하며 프로토타입 체인에 존재하는 모든 constructor를 검색하여 일치하는 constructor가 있다면 true를 반환한다.
function Person() {}
const person = new Person();
console.log(person instanceof Person); // true
console.log(person instanceof Object); // true
이를 이용해 css 함수에 타입 체크 기능을 추가해 보자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<script>
function getType(target) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(target).slice(8, -1);
}
function isString(target) {
return getType(target) === 'String';
}
function isElement(target) {
return !!(target && target instanceof HTMLElement);
// 또는 `nodeType`을 사용할 수도 있다.
// return !!(target && target.nodeType === 1);
}
// HTMLElement를 상속받은 모든 DOM 요소에 css 프로퍼티를 추가하고 값을 할당한다.
function css(elem, prop, val) {
// type checking
if (!(isElement(elem) && isString(prop) && isString(val))) {
throw new TypeError('매개변수의 타입이 맞지 않습니다.');
}
elem.style[prop] = val;
}
css(document.querySelector('p'), 'color', 'red');
css(document.querySelector('div'), 'color', 'red');
// TypeError: 매개변수의 타입이 맞지 않습니다.
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. 유사 배열 객체
배열인지 체크하기 위해서는 Array.isArray 메소드를 사용한다.
console.log(Array.isArray([])); // true
console.log(Array.isArray({})); // false
console.log(Array.isArray('123')); // false
유사 배열 객체(array-like object)은 length 프로퍼티를 갖는 객체로 문자열, arguments, HTMLCollection, NodeList 등은 유사 배열이다. 유사 배열 객체는 length 프로퍼티가 있으므로 순회할 수 있으며 call, apply 함수를 사용하여 배열의 메소드를 사용할 수도 있다.
어떤 객체가 유사 배열인지 체크하려면 우선 length 프로퍼티를 갖는지 length 프로퍼티의 값이 정상적인 값인지 체크한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
<script>
console.log(undefined == null)
const isArrayLike = function (collection) {
// 배열 인덱스: 32bit 정수(2의 32제곱 - 1)
// 유사 배열 인덱스: 자바스크립트로 표현할 수 있는 양의 정수(2의 53제곱 - 1)
const MAX_ARRAY_INDEX = Math.pow(2, 53) - 1;
// 빈문자열은 유사배열이다. undefined == null => true
const length = collection == null ? undefined : collection.length;
return typeof length === 'number' && length >= 0 && length <= MAX_ARRAY_INDEX;
};
// true
console.log(isArrayLike([]));
console.log(isArrayLike('abc'));
console.log(isArrayLike(''));
console.log(isArrayLike(document.querySelectorAll('li')));
console.log(isArrayLike(document.getElementsByName('li')));
console.log(isArrayLike({ length: 0 }));
(function () {
console.log(isArrayLike(arguments));
}());
// false
console.log(isArrayLike(123));
console.log(isArrayLike(document.querySelector('li')));
console.log(isArrayLike({ foo: 1 }));
console.log(isArrayLike());
console.log(isArrayLike(null));
</script>
</body>
</html>
