REST(Representational State Transfer)는 HTTP/1.0과 1.1의 스펙 작성에 참여하였고 아파치 HTTP 서버 프로젝트의 공동설립자인 로이 필딩 (Roy Fielding)의 2000년 논문에서 처음 소개되었다. 발표 당시의 웹이 HTTP의 설계 상 우수성을 제대로 사용하지 못하고 있는 상황을 보고 웹의 장점을 최대한 활용할 수 있는 아키텍쳐로서 REST를 소개하였고 이는 HTTP 프로토콜을 의도에 맞게 디자인하도록 유도하고 있다. REST의 기본 원칙을 성실히 지킨 서비스 디자인을 “RESTful”이라고 표현한다.
1. REST API 중심 규칙
REST에서 가장 중요한 기본적인 규칙은 두 가지이다. URI는 자원을 표현하는 데에 집중하고 행위에 대한 정의는 HTTP Method를 통해 하는 것이 REST한 API를 설계하는 중심 규칙이다.
1. URI는 정보의 자원을 표현해야 한다.
리소스명은 동사보다는 명사를 사용한다. URI는 자원을 표현하는데 중점을 두어야 한다. get 같은 행위에 대한 표현이 들어가서는 안된다.
# bad
GET /getTodos/1
GET /todos/show/1
# good
GET /todos/1
2. 자원에 대한 행위는 HTTP Method(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등)으로 표현한다.
# bad
GET /todos/delete/1
# good
DELETE /todos/1
2. HTTP Method
주로 5가지의 Method(GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE)를 사용하여 CRUD를 구현한다.
| Method | Action | 역할 | 페이로드 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | index/retrieve | 모든/특정 리소스를 조회 | x |
| POST | create | 리소스를 생성 | ○ |
| PUT | replace | 리소스의 전체를 교체 | ○ |
| PATCH | modify | 리소스의 일부를 수정 | ○ |
| DELETE | delete | 모든/특정 리소스를 삭제 | x |
3. REST API의 구성
REST API는 자원(Resource), 행위(Verb), 표현(Representations)의 3가지 요소로 구성된다. REST는 자체 표현 구조(Self-descriptiveness)로 구성되어 REST API만으로 요청을 이해할 수 있다.
| 구성 요소 | 내용 | 표현 방법 |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | 자원 | HTTP URI |
| Verb | 자원에 대한 행위 | HTTP Method |
| Representations | 자원에 대한 행위의 내용 | HTTP Message Pay Load |
4. REST API의 Example
4.1 json-server
json-server를 사용하여 REST API를 사용하여 보자.
$ mkdir rest-api-exam && cd rest-api-exam
$ npm init -y
$ npm install json-server
db.json 파일을 아래와 같이 생성한다.
{
"todos": [
{ "id": 1, "content": "HTML", "completed": false },
{ "id": 2, "content": "CSS", "completed": true },
{ "id": 3, "content": "Javascript", "completed": false }
]
}
npm script를 사용하여 json-server를 실행한다. 아래와 같이 package.json을 수정한다.
{
"name": "rest-api-exam",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"scripts": {
"start": "json-server --watch db.json --port 5000"
},
"dependencies": {
"json-server": "^0.15.0"
}
}
json-server를 실행한다. 포트는 5000을 사용한다.
$ npm start
4.2 GET
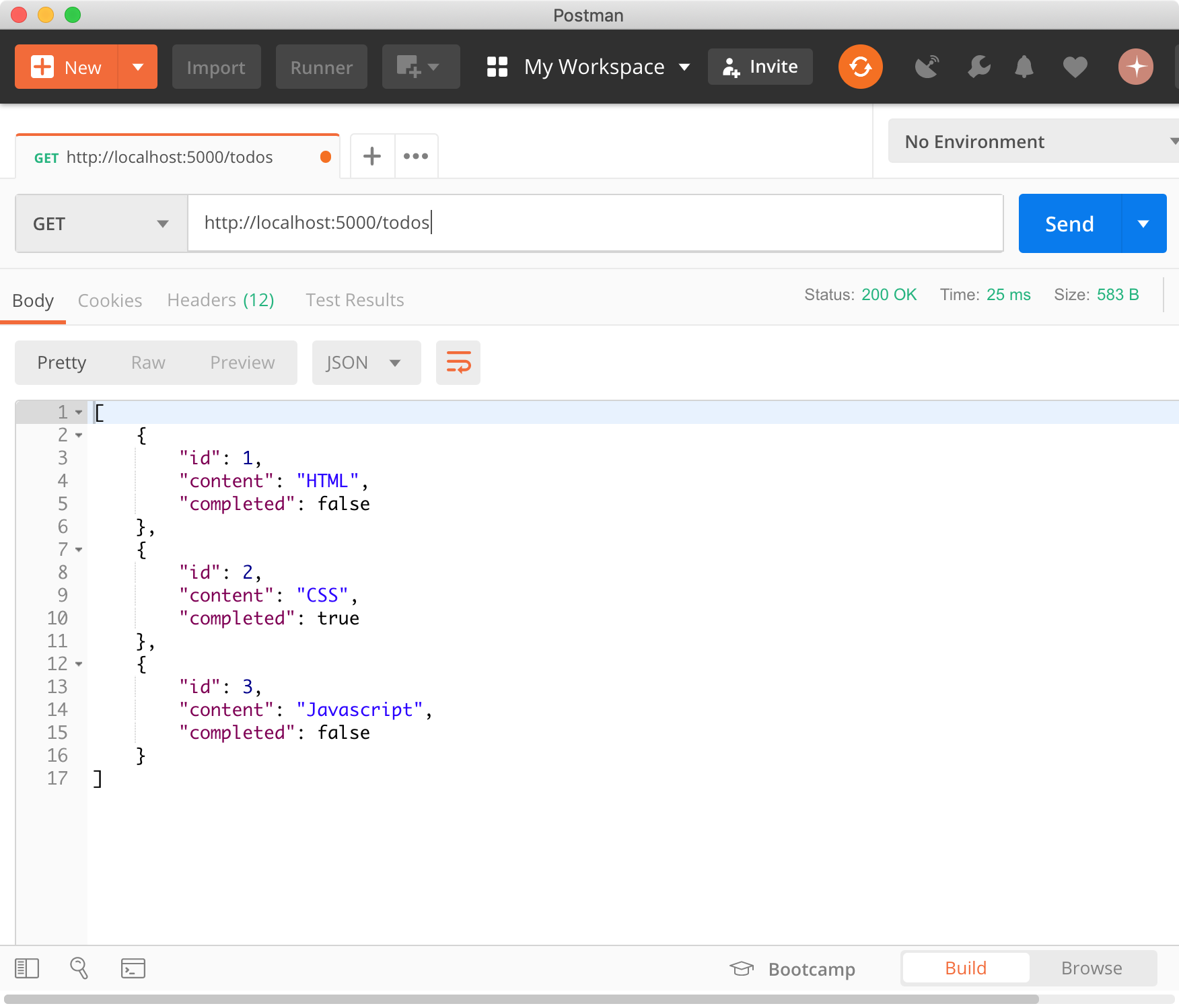
todos 리소스에서 모든 todo를 조회(index)한다.
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:5000/todos
[
{
"id": 1,
"content": "HTML",
"completed": false
},
{
"id": 2,
"content": "CSS",
"completed": true
},
{
"id": 3,
"content": "Javascript",
"completed": false
}
]
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:5000/todos');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 200) { // 200: OK => https://httpstatuses.com
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
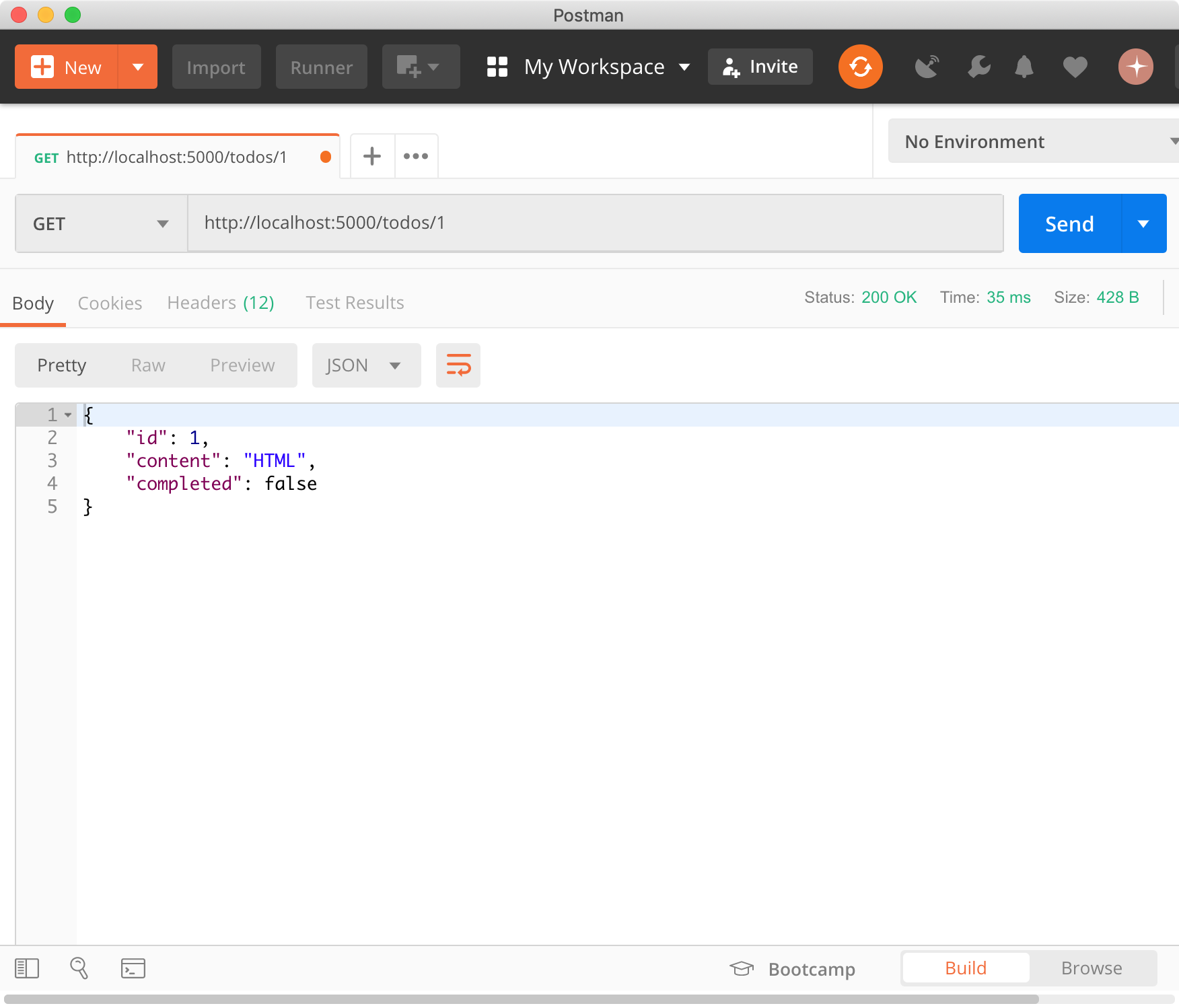
todos 리소스에서 id를 사용하여 특정 todo를 조회(retrieve)한다.
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:5000/todos/1
{
"id": 1,
"content": "HTML",
"completed": false
}
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', 'http://localhost:5000/todos/1');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
4.3 POST
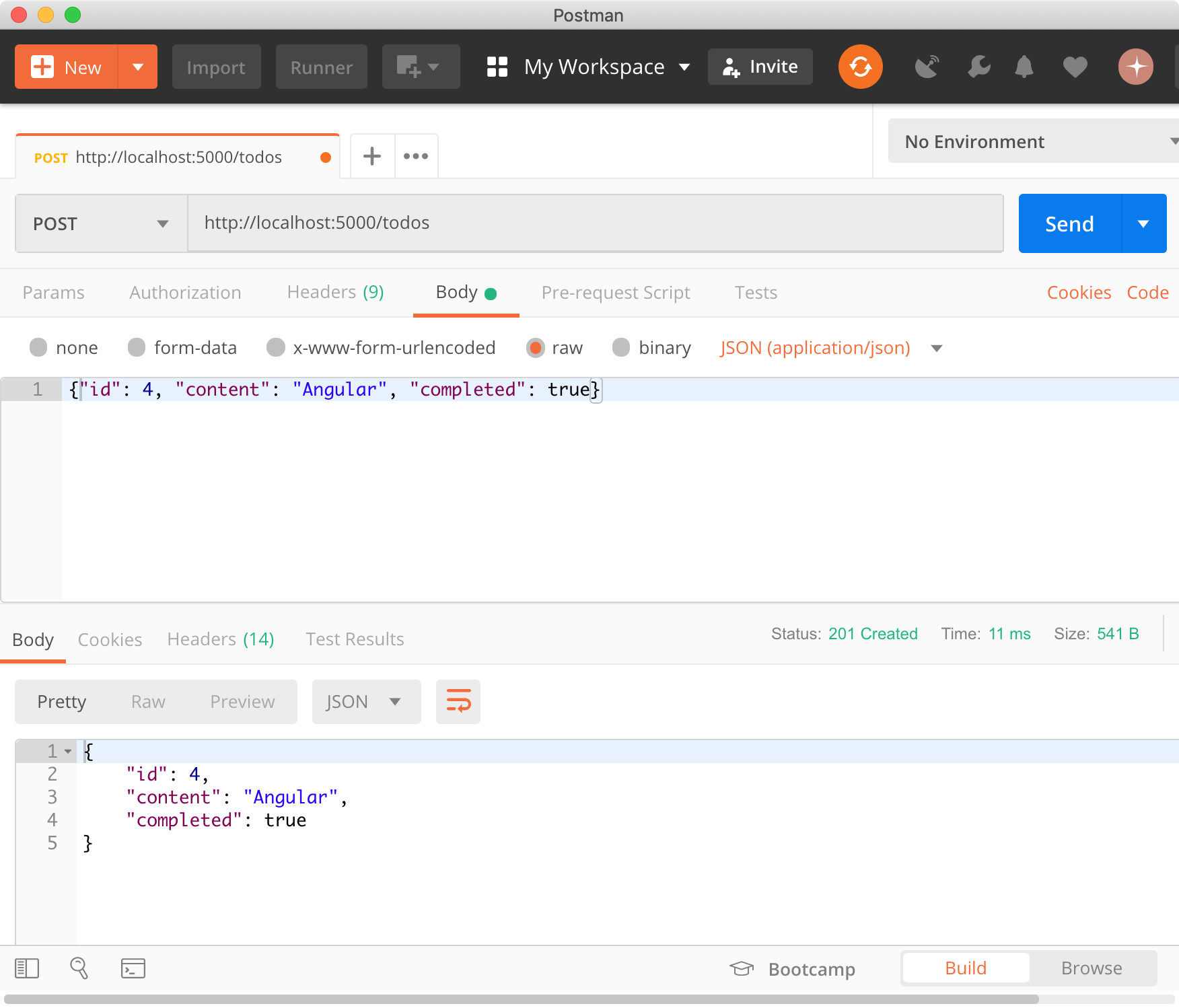
todos 리소스에 새로운 todo를 생성한다.
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/todos -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id": 4, "content": "Angular", "completed": true}'
{
"id": 4,
"content": "Angular",
"completed": true
}
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('POST', 'http://localhost:5000/todos');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({ id: 4, content: 'Angular', completed: true }));
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 201) { // 201: Created
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
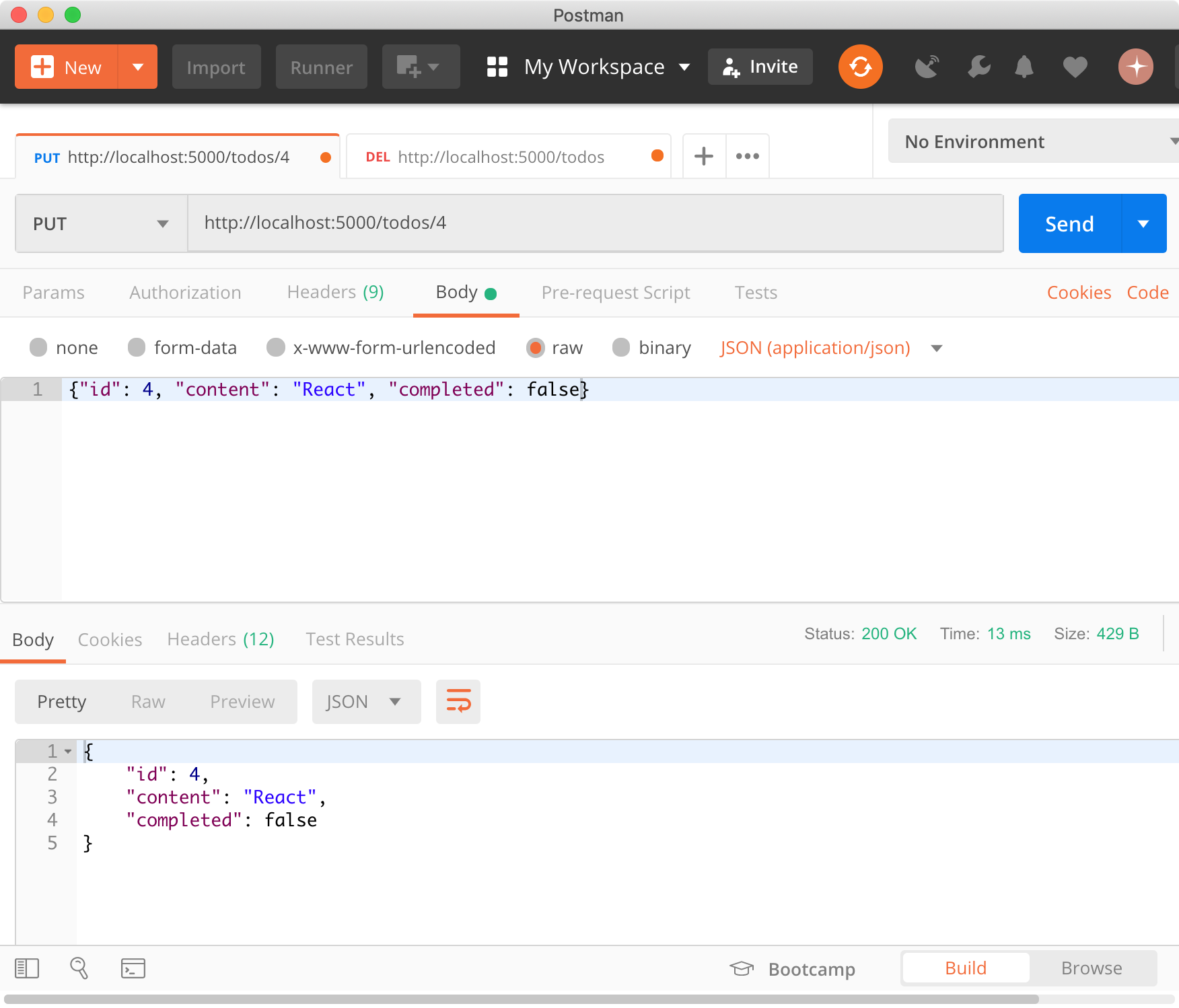
4.4 PUT
PUT은 특정 리소스의 전체를 갱신할 때 사용한다. todos 리소스에서 id를 사용하여 todo를 특정하여 id를 제외한 리소스 전체를 갱신한다.
$ curl -X PUT http://localhost:5000/todos/4 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id": 4, "content": "React", "completed": false}'
{
"content": "React",
"completed": false,
"id": 4
}
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('PUT', 'http://localhost:5000/todos/4');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({ id: 4, content: 'React', completed: false }));
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
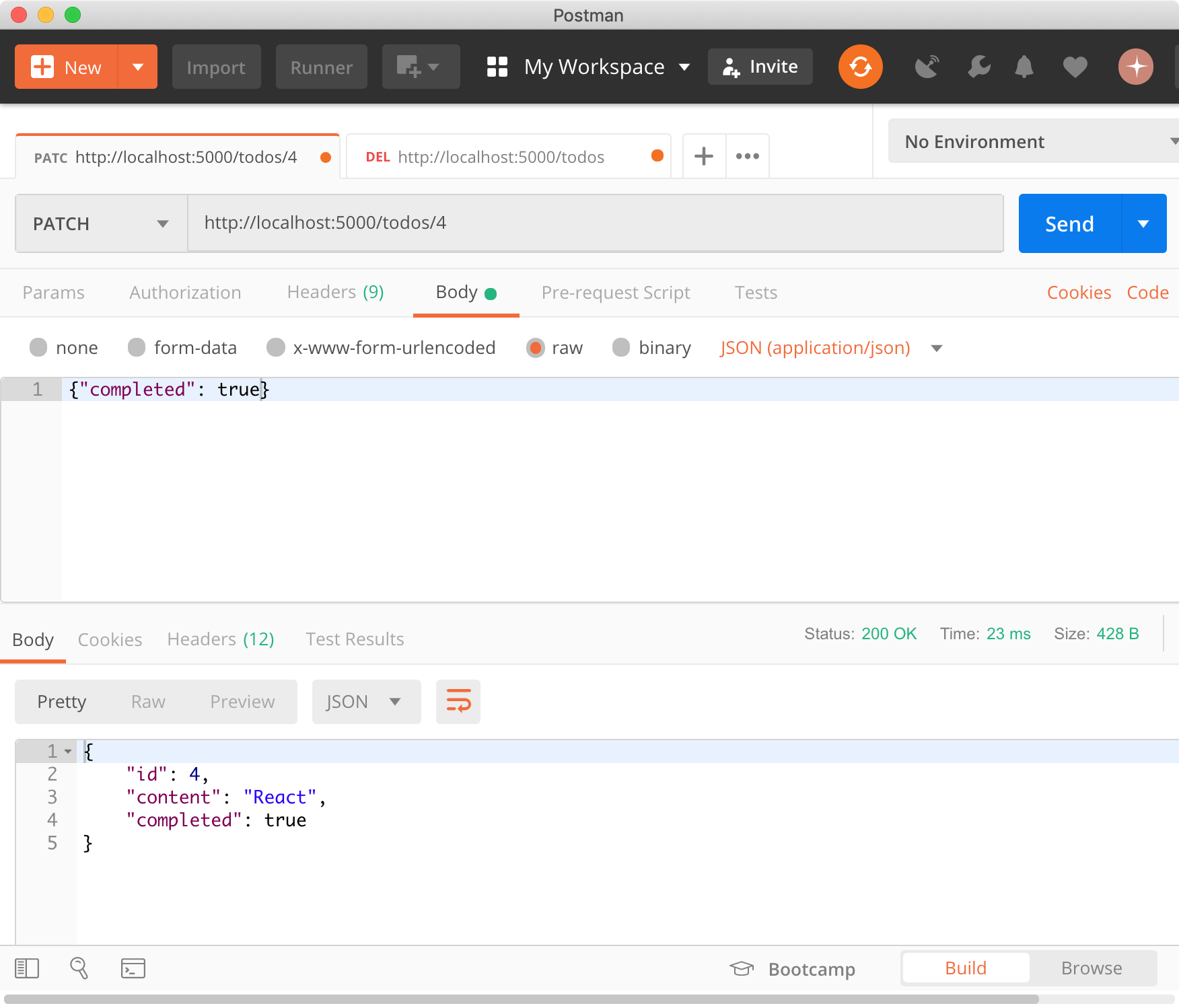
4.5 PATCH
PATCH는 특정 리소스의 일부를 갱신할 때 사용한다. todos 리소스의 id를 사용하여 todo를 특정하여 completed만을 true로 갱신한다.
$ curl -X PATCH http://localhost:5000/todos/4 -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"completed": true}'
{
"id": 4,
"content": "React",
"completed": true
}
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('PATCH', 'http://localhost:5000/todos/4');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({ completed: true }));
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
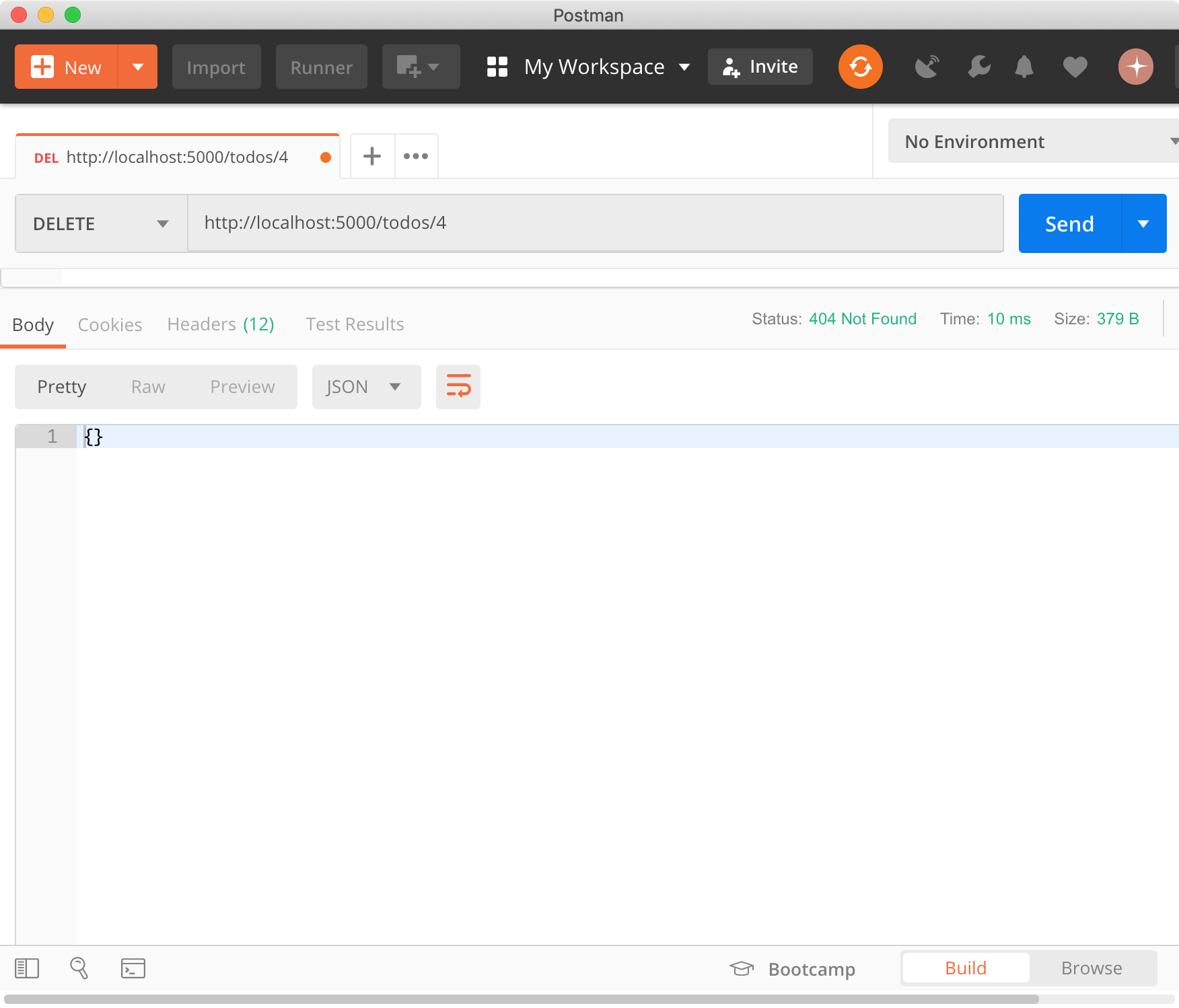
4.6 DELETE
todos 리소스에서 id를 사용하여 todo를 특정하고 삭제한다.
$ curl -X DELETE http://localhost:5000/todos/4
{}
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('DELETE', 'http://localhost:5000/todos/4');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (e) {
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return;
if(xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
} else {
console.log("Error!");
}
};
