1. 상속(Inheritance)
상속이란 상위(부모, 조상) 요소에 적용된 프로퍼티를 하위(자식, 자손) 요소가 물려 받는 것을 의미한다. 상속 기능이 없다면 각 요소의 Rule set에 프로퍼티를 매번 각각 지정해야 한다.
하지만 모든 프로퍼티가 상속되는 것은 아니다. 프로퍼티 중에는 상속이 되는 것과 되지 않는 것이 있다.
| property | Inherit |
|---|---|
| width/height | no |
| margin | no |
| padding | no |
| border | no |
| box-sizing | no |
| display | no |
| visibility | yes |
| opacity | yes |
| background | no |
| font | yes |
| color | yes |
| line-height | yes |
| text-align | yes |
| vertical-align | no |
| text-decoration | no |
| white-space | yes |
| position | no |
| top/right/bottom/left | no |
| z-index | no |
| overflow | no |
| float | no |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.text-red {
color: red;
border: 1px solid #bcbcbc;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="text-red">
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>Paragraph<strong>strong</strong></p>
<button>Button</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
color는 상속되는 프로퍼티로서 자식 요소는 물론 자손 요소까지 적용된다. 하지만 button처럼 요소에 따라 상속 받지 않는 경우도 존재한다.
border, padding은 상속되지 않는 요소로 하위 요소에 적용되지 않는다. W3C가 제공하는 Full property table의 Inherited?가 yes인 프로퍼티만 상속된다.
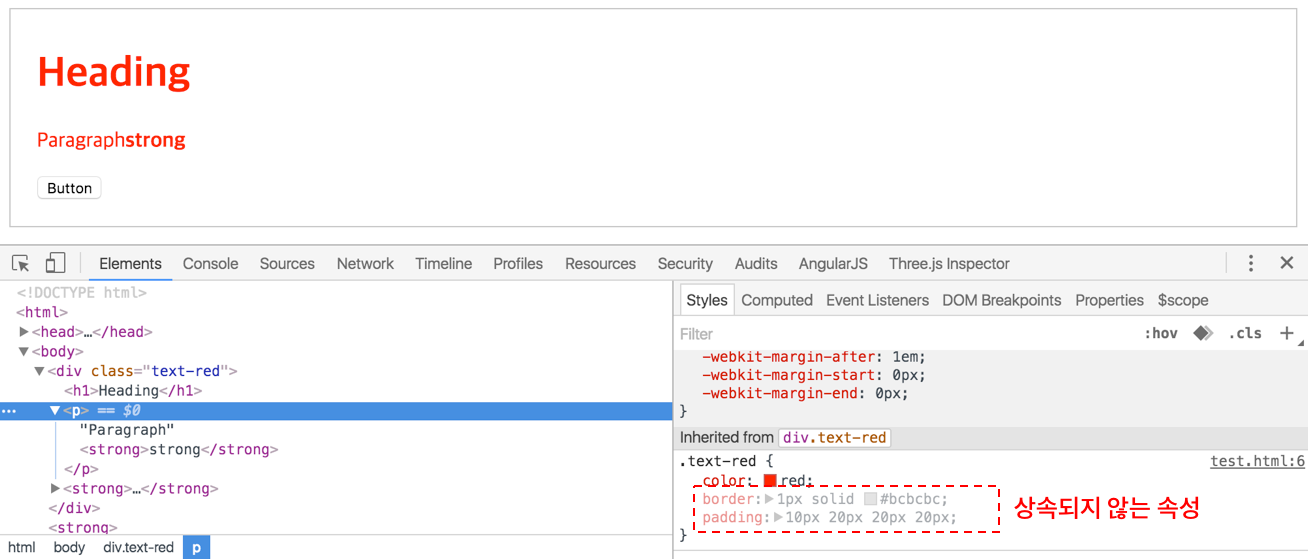
상속되지 않는 프로퍼티
상속되지 않는 경우(상속받지 않는 요소 또는 상속되지 않는 프로퍼티), inherit 키워드를 사용하여 명시적으로 상속받게 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.text-red {
color: red;
border: 1px solid #bcbcbc;
padding: 10px;
}
.text-red button {
color: inherit;
}
.text-red p {
border: inherit;
padding: inherit;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="text-red">
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>Paragraph<strong>strong</strong></p>
<button>Button</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2. 캐스캐이딩(Cascading)
요소는 하나 이상의 CSS 선언에 영향을 받을 수 있다. 이때 충돌을 피하기 위해 CSS 적용 우선순위가 필요한데 이를 캐스캐이딩(Cascading Order)이라고 한다.
캐스캐이딩에는 다음과 같이 세가지 규칙이 있다.
- 중요도
- CSS가 어디에 선언 되었는지에 따라서 우선순위가 달라진다.
- 명시도
- 대상을 명확하게 특정할수록 명시도가 높아지고 우선순위가 높아진다.
- 선언순서
- 선언된 순서에 따라 우선 순위가 적용된다. 즉, 나중에 선언된 스타일이 우선 적용된다.
2.1 중요도
CSS가 어디에 선언 되었는지에 따라서 우선순위가 달라진다.
- head 요소 내의 style 요소
- head 요소 내의 style 요소 내의
@import문 <link>로 연결된 CSS 파일<link>로 연결된 CSS 파일 내의@import문- 브라우저 디폴트 스타일시트
/* style.css */
body {
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<style>
body {
background-color: beige;
color: navy;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
</body>
</html>
2.2 명시도
대상을 명확하게 특정할수록 명시도가 높아지고 우선순위가 높아진다.
!important > 인라인 스타일 > 아이디 선택자 > 클래스/어트리뷰트/가상 선택자 > 태그 선택자 > 전체 선택자 > 상위 요소에 의해 상속된 속성
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p { color: red !important; }
#thing { color: blue; }
div.food { color: chocolate; }
.food { color: green; }
div { color: orange; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="thing">Will be Red.</p>
<div class="food">Will be Chocolate.</div>
</body>
</html>
2.3 선언순서
선언된 순서에 따라 우선 순위가 적용된다. 즉, 나중에 선언된 스타일이 우선 적용된다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p { color: blue; }
p { color: red; }
.red { color: red; }
.blue { color: blue; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Will be RED.</p>
<p class="blue red">Will be BLUE.</p>
</body>
</html>
